Changes in PRIMAP-hist v2.6_final compared to v2.5.1_final for Hungary
2024-09-24
Johannes Gütschow
Change analysis for Hungary for PRIMAP-hist v2.6_final compared to v2.5.1_final
Overview over emissions by sector and gas
The following figures show the aggregate national total emissions excluding LULUCF AR6GWP100 for the country reported priority scenario. The dotted linesshow the v2.5.1_final data.
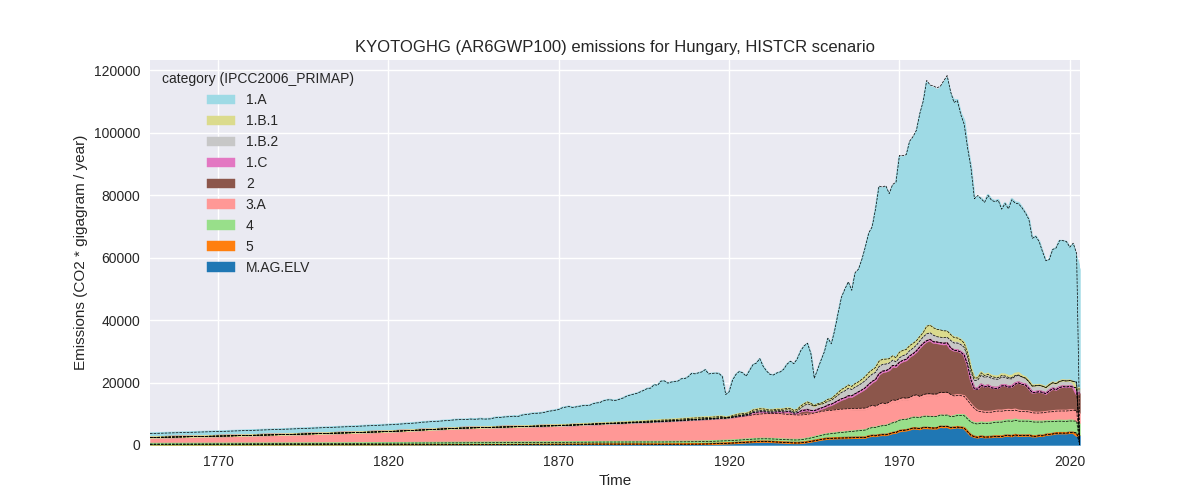
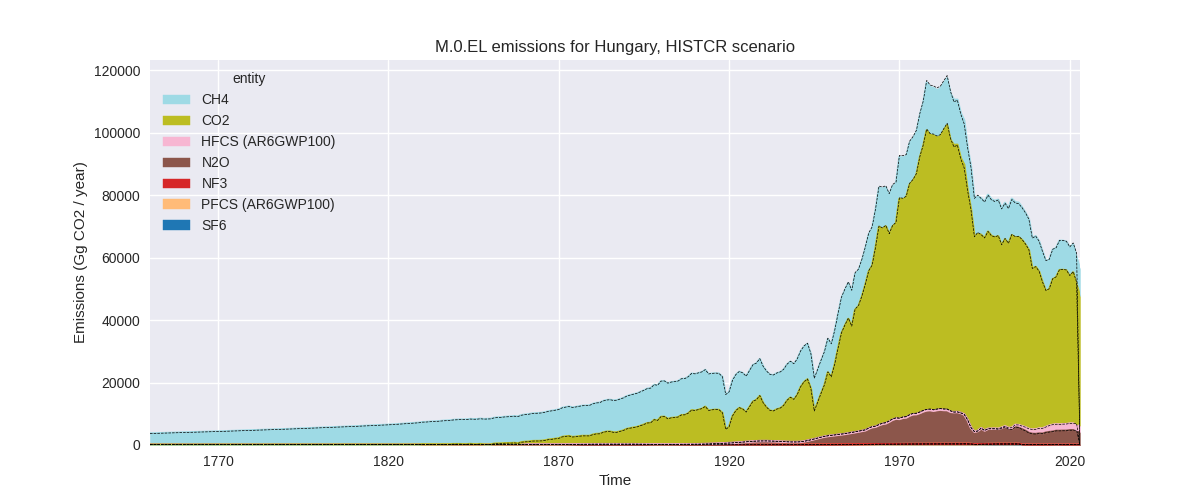
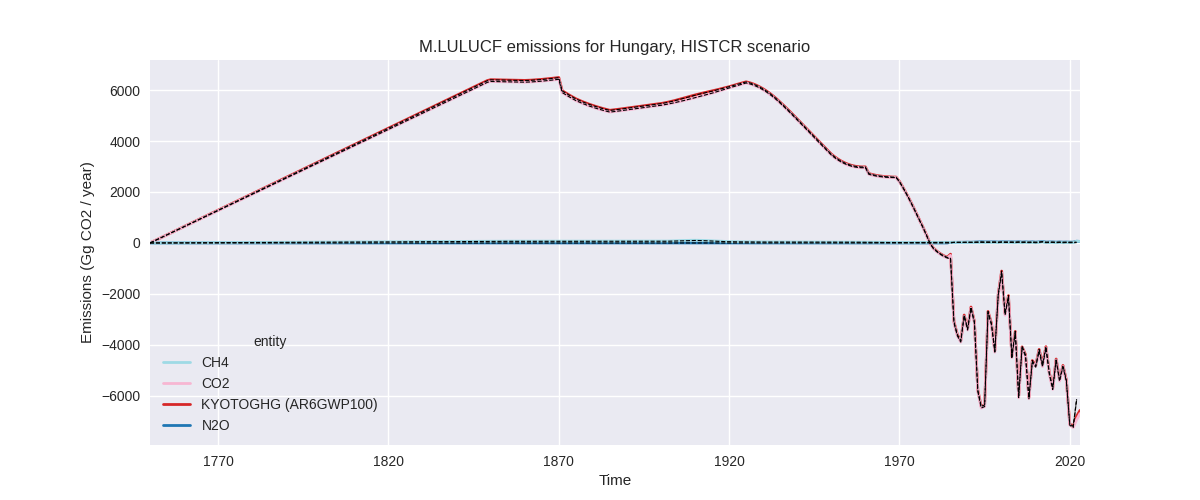
The following figures show the aggregate national total emissions excluding LULUCF AR6GWP100 for the third party priority scenario. The dotted linesshow the v2.5.1_final data.
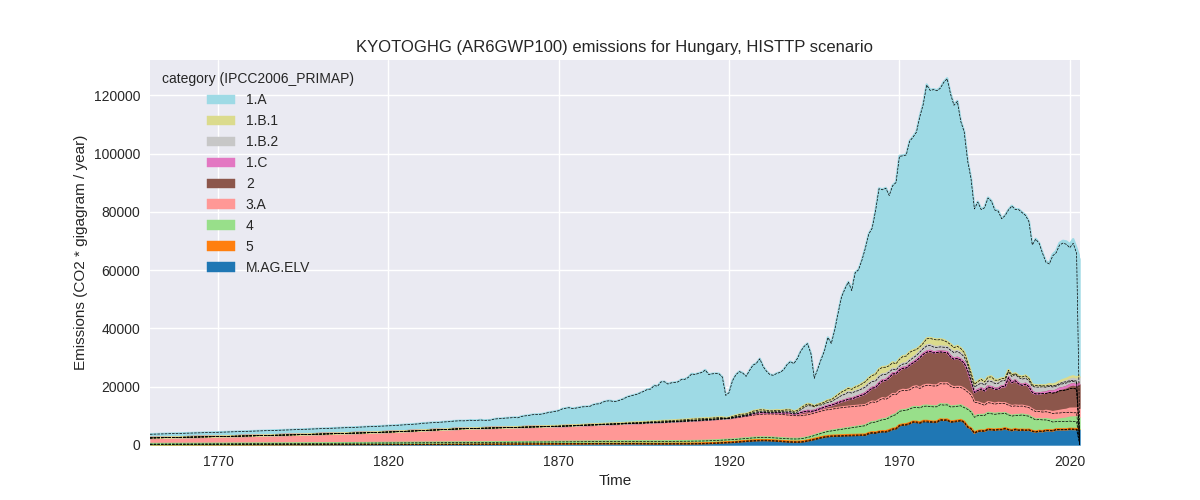
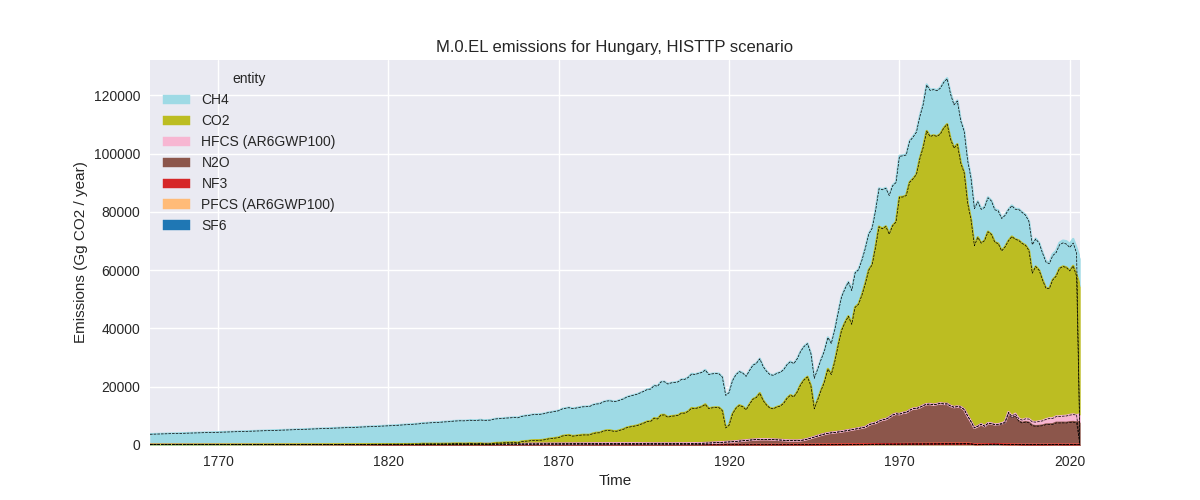
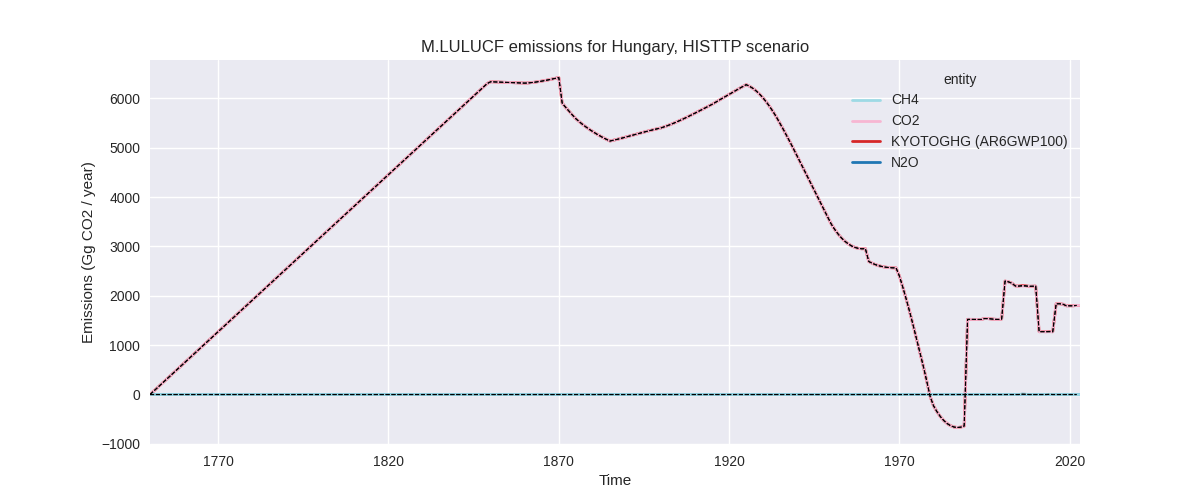
Overview over changes
In the country reported priority scenario we have the following changes for aggregate Kyoto GHG and national total emissions excluding LULUCF (M.0.EL):
- Emissions in 2022 have changed by -2.4%% (-1452.47 Gg CO2 / year)
- Emissions in 1990-2022 have changed by -0.1%% (-61.09 Gg CO2 / year)
In the third party priority scenario we have the following changes for aggregate Kyoto GHG and national total emissions excluding LULUCF (M.0.EL):
- Emissions in 2022 have changed by 2.5%% (1648.11 Gg CO2 / year)
- Emissions in 1990-2022 have changed by 0.4%% (336.69 Gg CO2 / year)
Most important changes per scenario and time frame
In the country reported priority scenario the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 2022 (top 5):
- 1: 1.A, CO2 with 882.59 Gg CO2 / year (2.2%)
- 2: M.AG.ELV, N2O with -827.78 Gg CO2 / year (-22.8%)
- 3: 2, CO2 with -811.53 Gg CO2 / year (-17.8%)
- 4: 1.B.2, CH4 with -399.18 Gg CO2 / year (-23.4%)
- 5: 3.A, CH4 with -163.93 Gg CO2 / year (-5.2%)
In the country reported priority scenario the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 1990-2022 (top 5):
- 1: 4, CH4 with 164.18 Gg CO2 / year (4.0%)
- 2: 1.A, CO2 with -143.47 Gg CO2 / year (-0.3%)
- 3: 3.A, CH4 with -74.48 Gg CO2 / year (-2.3%)
- 4: 1.B.2, CH4 with 57.45 Gg CO2 / year (2.7%)
- 5: M.AG.ELV, N2O with -46.74 Gg CO2 / year (-1.6%)
In the third party priority scenario the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 2022 (top 5):
- 1: 4, CH4 with 1378.46 Gg CO2 / year (58.3%)
- 2: 1.A, CO2 with 408.76 Gg CO2 / year (1.0%)
- 3: 2, HFCS (AR6GWP100) with -165.21 Gg CO2 / year (-6.3%)
- 4: 4, N2O with 33.15 Gg CO2 / year (18.9%)
- 5: 4, CO2 with -14.96 Gg CO2 / year (-47.9%)
In the third party priority scenario the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 1990-2022 (top 5):
- 1: 4, CH4 with 313.00 Gg CO2 / year (7.6%)
- 2: 4, N2O with 17.31 Gg CO2 / year (11.0%)
- 3: 1.A, CO2 with 12.25 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 4: 4, CO2 with -7.56 Gg CO2 / year (-10.5%)
- 5: 2, HFCS (AR6GWP100) with -5.01 Gg CO2 / year (-0.5%)
Notes on data changes
Here we list notes explaining important emissions changes for the country. ’' means that the following text only applies to the TP time series, while means that it only applies to the CR scenario. Otherwise the note applies to both scenarios.
- We have added EEA 2024 inventory data.
- N2O in M.AG.ELV is over 20% lower in 2022 because of a steep emissions decline in EEA 2024 (CR)
- Energy CO2 emissions are slightly higher in 2022 because the EEA2024 and EI2024 growth rates for 2022 are higher than the EI2023 growth rates (TP, CR)
- Fugitive CH4 from oil and gas (1.B.2) is much lower in the last years (and slightly lower cumulatively) because EEA2024 emissions are lower than CRF2023 (CR)
- Waste CH4 is 4% higher cumulatively because emissions in EEA2024 are higher than in CRF2023 (CR scenario)
- HFCs are lower in 2022 because of an emissions decline for 2022 in EEA2024
- Changes in sectors 4 and 5 in the TP scenario are due to the removal of FAOSTAT data.
Changes by sector and gas
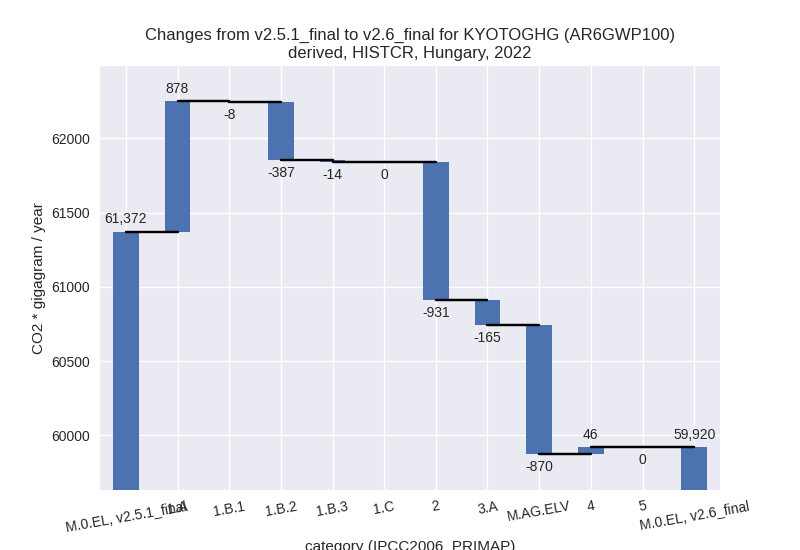
For each scenario and time frame the changes are displayed for all individual sectors and all individual gases. In the sector plot we use aggregate Kyoto GHGs in AR6GWP100. In the gas plot we usenational total emissions without LULUCF. ## country reported scenario
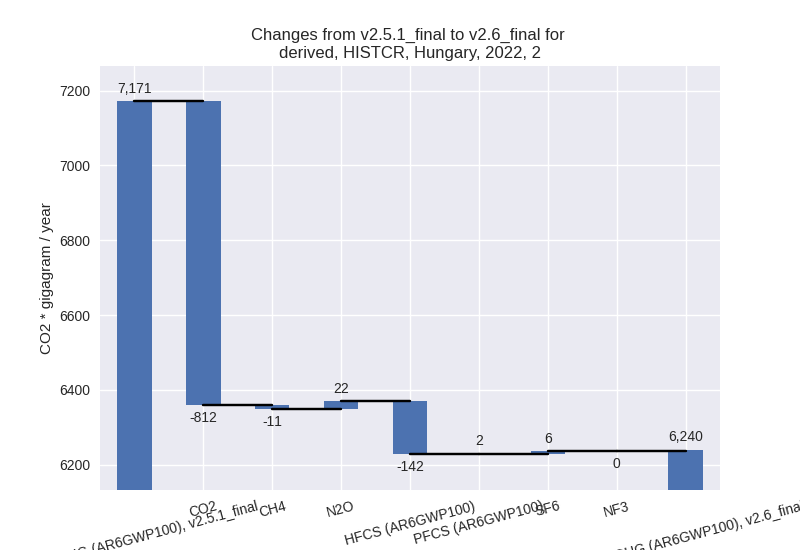
2022
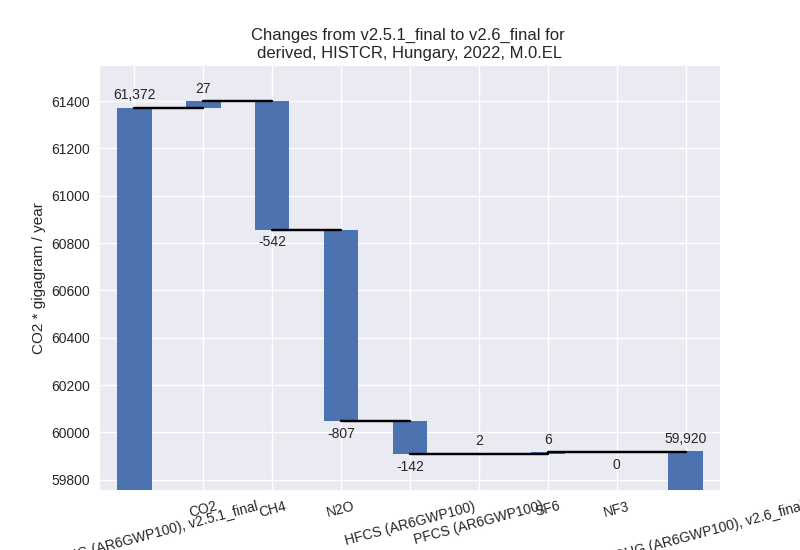
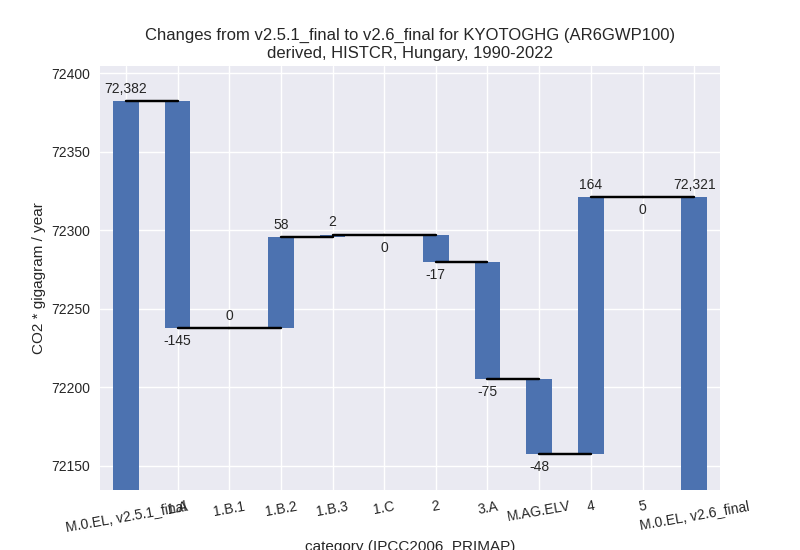
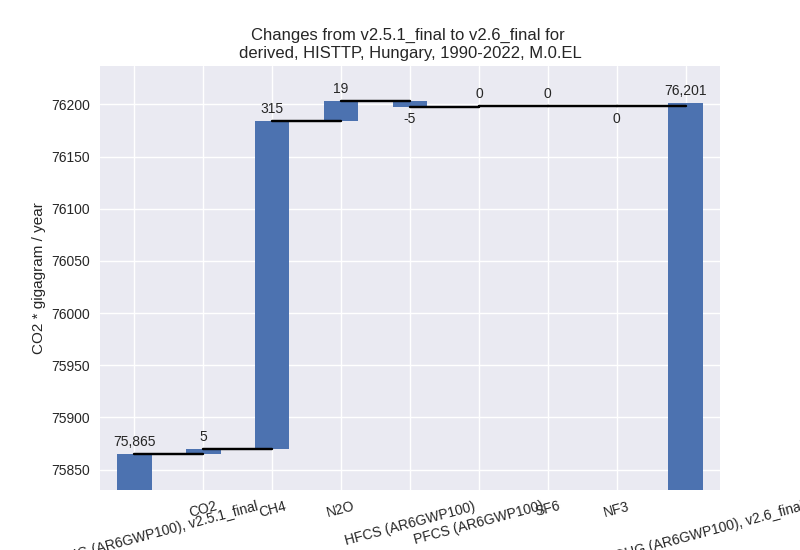
1990-2022
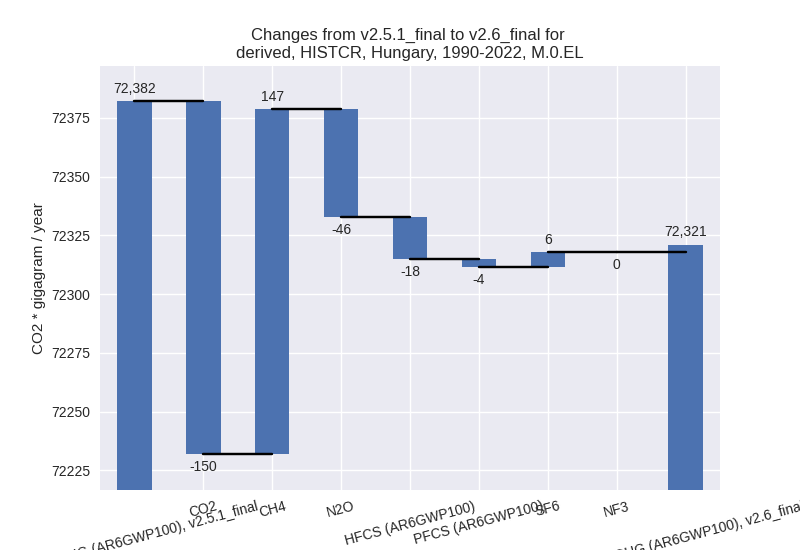
third party scenario
2022
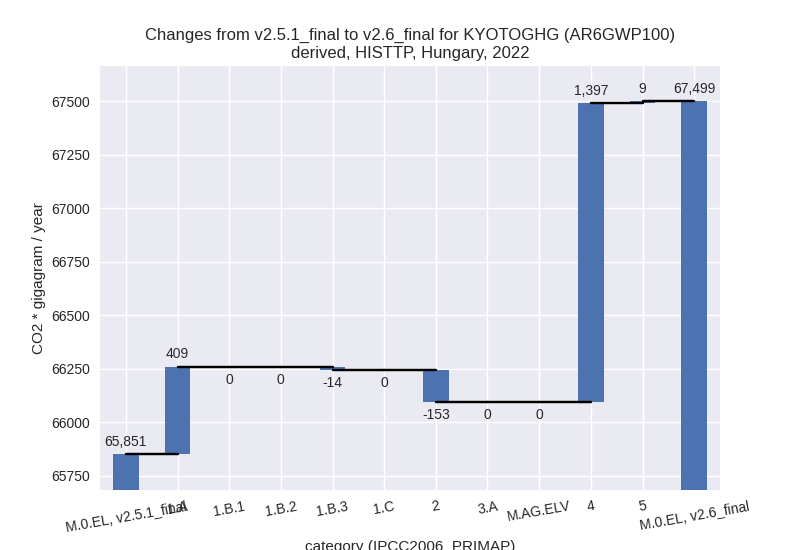
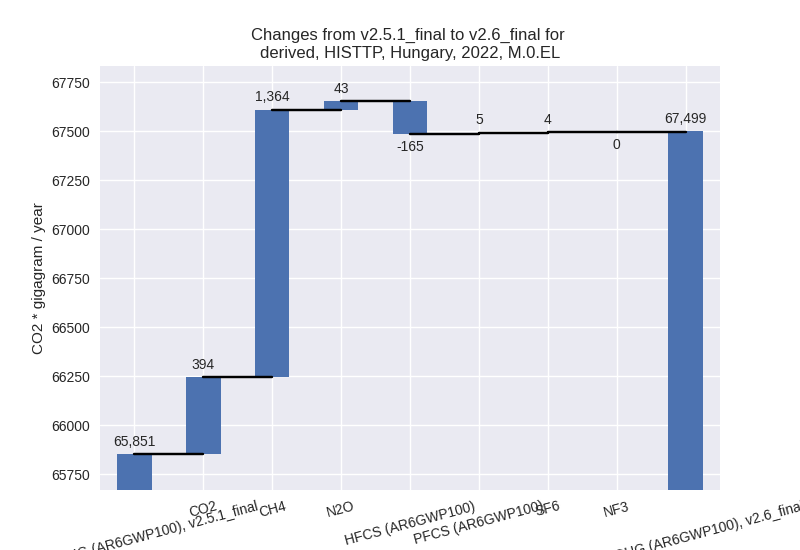
1990-2022
Detailed changes for the scenarios:
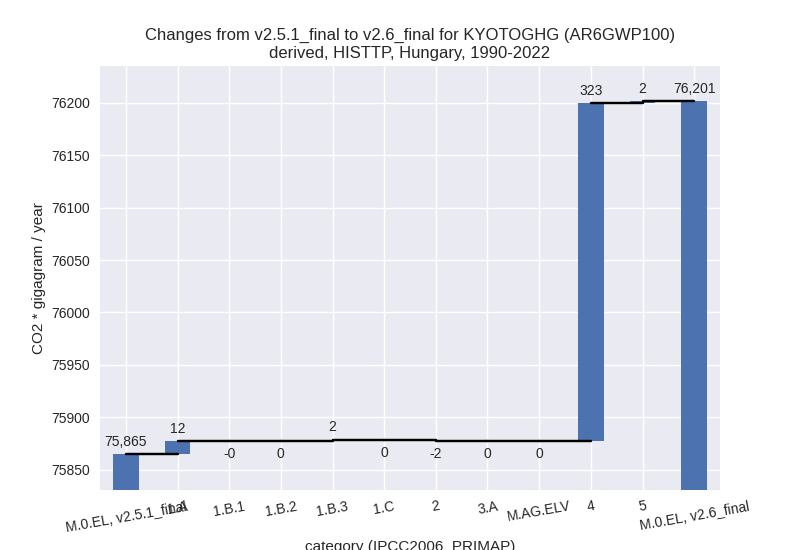
country reported scenario (HISTCR):
Most important changes per time frame
For 2022 the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 2022 (top 5):
- 1: 1.A, CO2 with 882.59 Gg CO2 / year (2.2%)
- 2: M.AG.ELV, N2O with -827.78 Gg CO2 / year (-22.8%)
- 3: 2, CO2 with -811.53 Gg CO2 / year (-17.8%)
- 4: 1.B.2, CH4 with -399.18 Gg CO2 / year (-23.4%)
- 5: 3.A, CH4 with -163.93 Gg CO2 / year (-5.2%)
For 1990-2022 the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 1990-2022 (top 5):
- 1: 4, CH4 with 164.18 Gg CO2 / year (4.0%)
- 2: 1.A, CO2 with -143.47 Gg CO2 / year (-0.3%)
- 3: 3.A, CH4 with -74.48 Gg CO2 / year (-2.3%)
- 4: 1.B.2, CH4 with 57.45 Gg CO2 / year (2.7%)
- 5: M.AG.ELV, N2O with -46.74 Gg CO2 / year (-1.6%)
Changes in the main sectors for aggregate KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) are
- 1: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 43573.92 Gg CO2 / year which is 72.7% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have changed by 1.1% (468.48 Gg CO2 / year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by -0.2% (-85.10 Gg CO2 / year).
- 2: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 6239.95 Gg
CO2 / year which is 10.4% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have
changed by -13.0% (-931.39 Gg CO2 /
year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by -0.2% (-17.12 Gg CO2 / year). For 2022 the
changes per gas
are:
- M.AG: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 6292.43
Gg CO2 / year which is 10.5% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have
changed by -14.1% (-1035.53 Gg CO2 /
year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by -1.8% (-122.60 Gg CO2 / year). For 2022
the changes per gas
are:
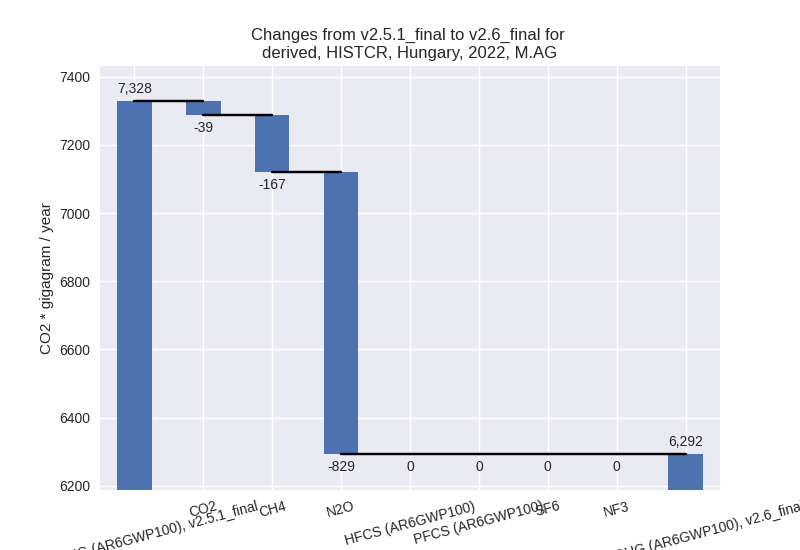
The changes come from the following subsectors:- 3.A: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 3257.29
Gg CO2 / year which is 51.8% of category M.AG emissions. 2022 Emissions
have changed by -4.8% (-165.36 Gg
CO2 / year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by -2.1% (-74.57 Gg CO2 / year). For 2022 the
changes per gas
are:
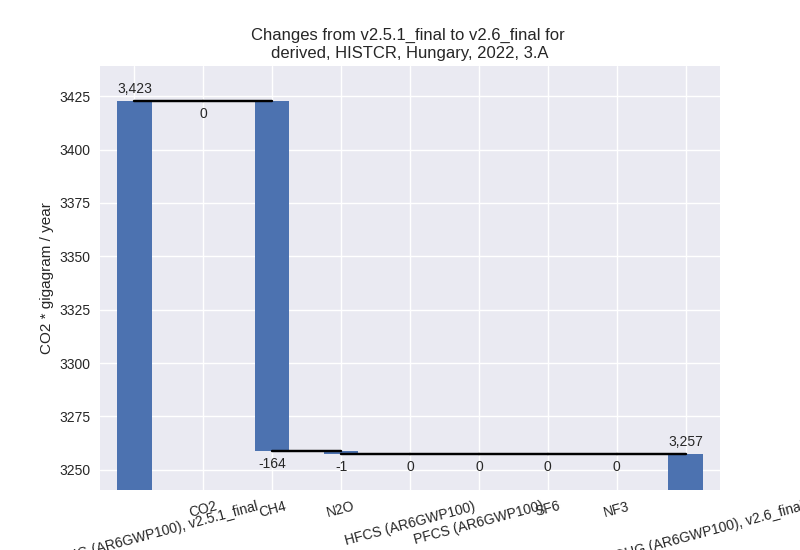
For 1990-2022 the changes per gas are: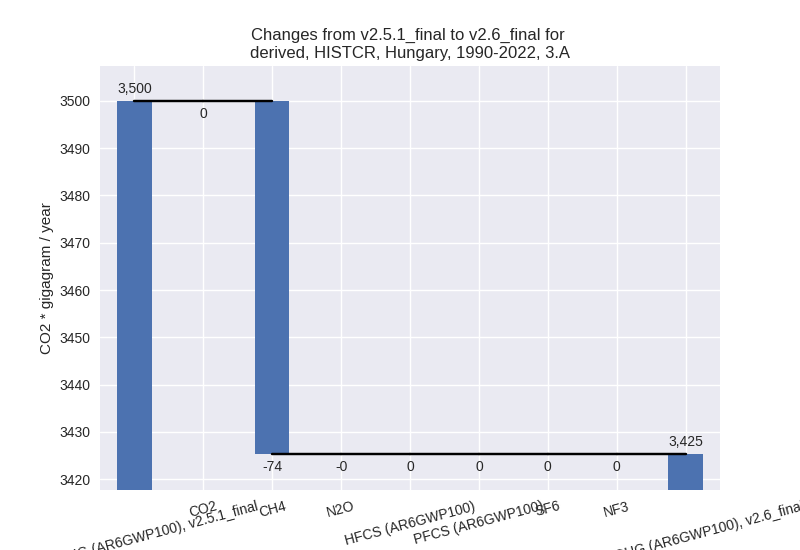
There is no subsector information available in PRIMAP-hist. - M.AG.ELV: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are
3035.14 Gg CO2 / year which is 48.2% of category M.AG emissions. 2022
Emissions have changed by -22.3%
(-870.17 Gg CO2 / year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by -1.5% (-48.03 Gg CO2 / year). For 2022 the
changes per gas
are:
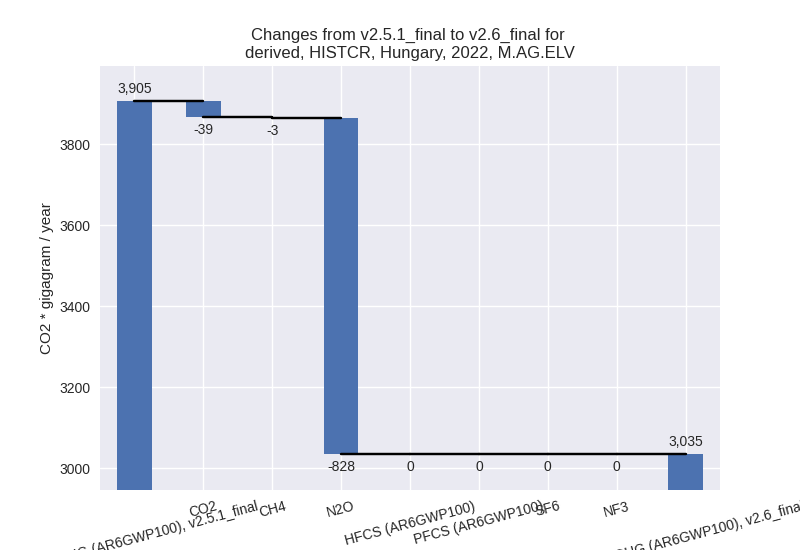
There is no subsector information available in PRIMAP-hist.
- 3.A: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 3257.29
Gg CO2 / year which is 51.8% of category M.AG emissions. 2022 Emissions
have changed by -4.8% (-165.36 Gg
CO2 / year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by -2.1% (-74.57 Gg CO2 / year). For 2022 the
changes per gas
are:
- 4: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 3813.49 Gg
CO2 / year which is 6.4% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have
changed by 1.2% (45.97 Gg CO2 /
year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by 3.8% (163.73 Gg CO2 / year). For 1990-2022
the changes per gas
are:
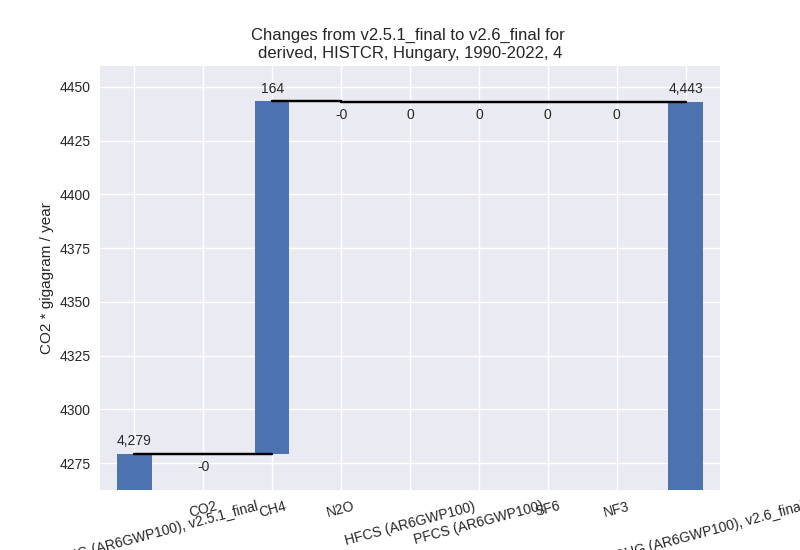
- 5: No data
third party scenario (HISTTP):
Most important changes per time frame
For 2022 the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 2022 (top 5):
- 1: 4, CH4 with 1378.46 Gg CO2 / year (58.3%)
- 2: 1.A, CO2 with 408.76 Gg CO2 / year (1.0%)
- 3: 2, HFCS (AR6GWP100) with -165.21 Gg CO2 / year (-6.3%)
- 4: 4, N2O with 33.15 Gg CO2 / year (18.9%)
- 5: 4, CO2 with -14.96 Gg CO2 / year (-47.9%)
For 1990-2022 the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 1990-2022 (top 5):
- 1: 4, CH4 with 313.00 Gg CO2 / year (7.6%)
- 2: 4, N2O with 17.31 Gg CO2 / year (11.0%)
- 3: 1.A, CO2 with 12.25 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 4: 4, CO2 with -7.56 Gg CO2 / year (-10.5%)
- 5: 2, HFCS (AR6GWP100) with -5.01 Gg CO2 / year (-0.5%)
Changes in the main sectors for aggregate KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) are
- 1: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 47040.43 Gg CO2 / year which is 69.7% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have changed by 0.8% (394.58 Gg CO2 / year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by 0.0% (13.80 Gg CO2 / year).
- 2: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 7974.52 Gg CO2 / year which is 11.8% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have changed by -1.9% (-152.51 Gg CO2 / year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by -0.0% (-1.63 Gg CO2 / year).
- M.AG: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 8373.59 Gg CO2 / year which is 12.4% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have changed by 0.0% (0.00 Gg CO2 / year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by 0.0% (0.00 Gg CO2 / year).
- 4: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 3968.10 Gg
CO2 / year which is 5.9% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have
changed by 54.3% (1396.65 Gg CO2 /
year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by 7.5% (322.75 Gg CO2 / year). For 2022 the
changes per gas
are:
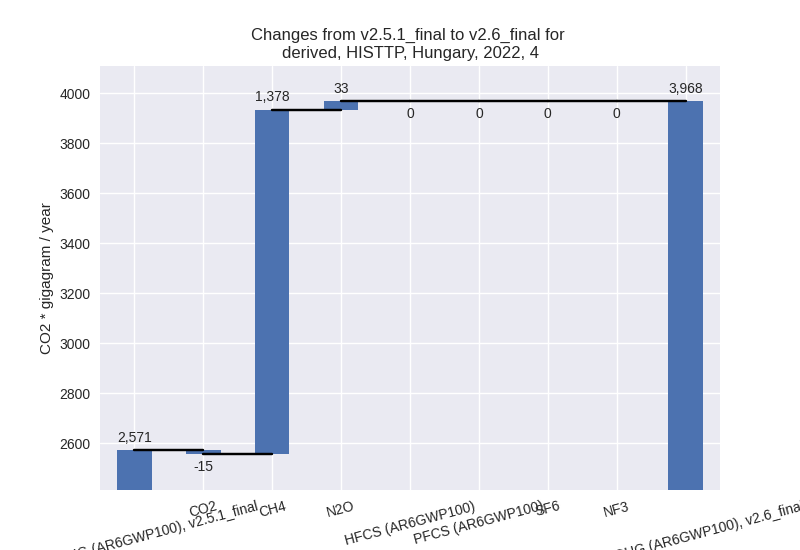
For 1990-2022 the changes per gas are: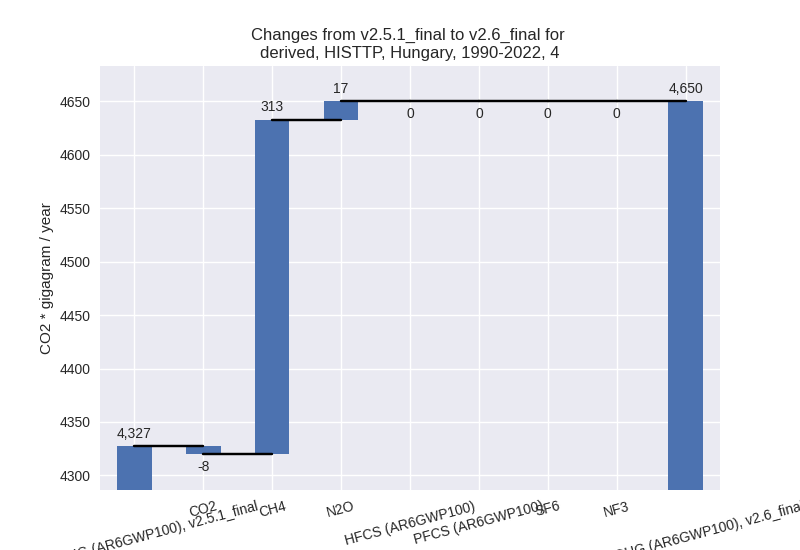
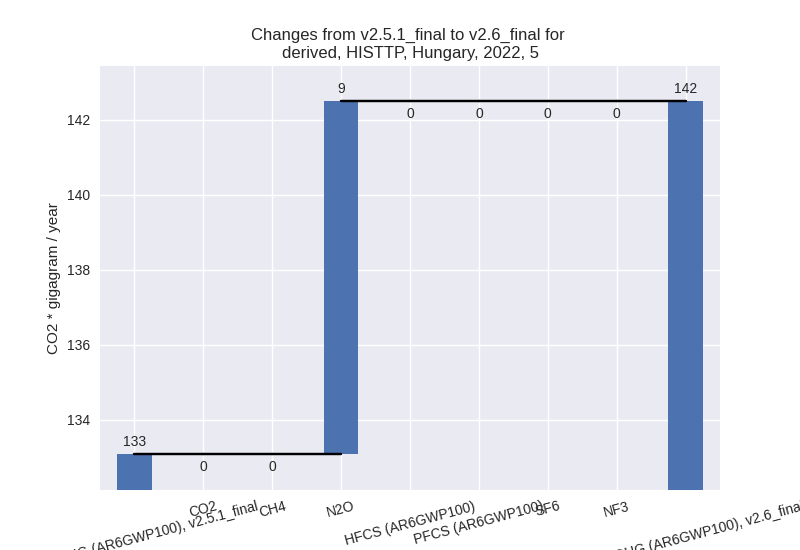
- 5: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 142.48 Gg
CO2 / year which is 0.2% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have
changed by 7.1% (9.40 Gg CO2 /
year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by 0.9% (1.77 Gg CO2 / year). For 2022 the
changes per gas
are: