Changes in PRIMAP-hist v2.6_final compared to v2.5.1_final for Korea, Republic of
2024-09-24
Johannes Gütschow
Change analysis for Korea, Republic of for PRIMAP-hist v2.6_final compared to v2.5.1_final
Overview over emissions by sector and gas
The following figures show the aggregate national total emissions excluding LULUCF AR6GWP100 for the country reported priority scenario. The dotted linesshow the v2.5.1_final data.
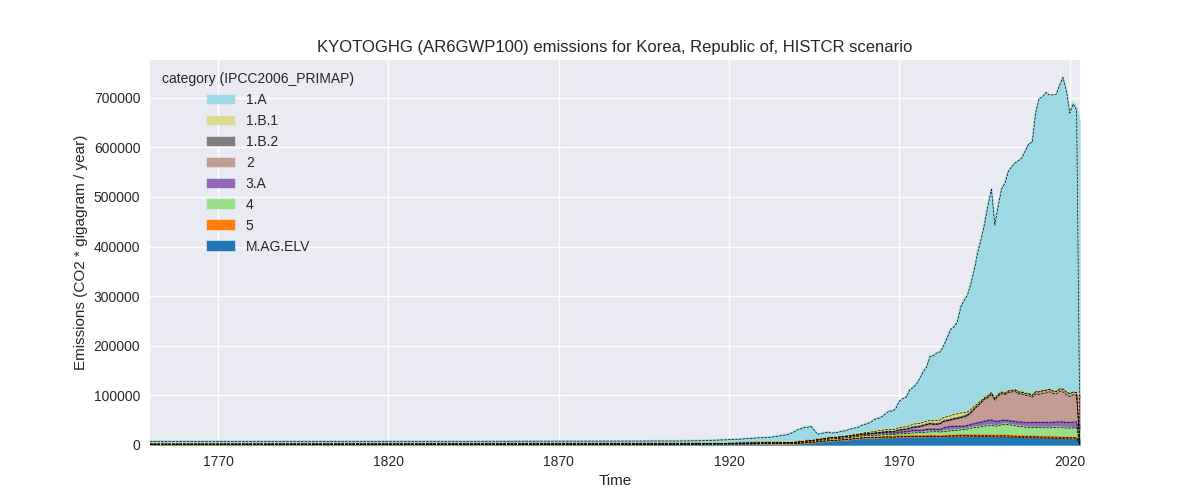
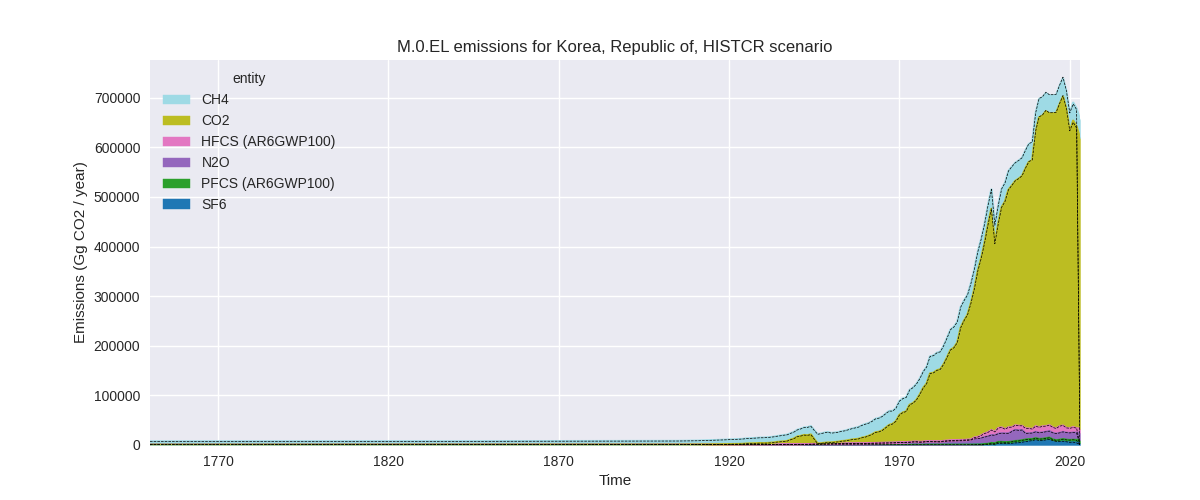
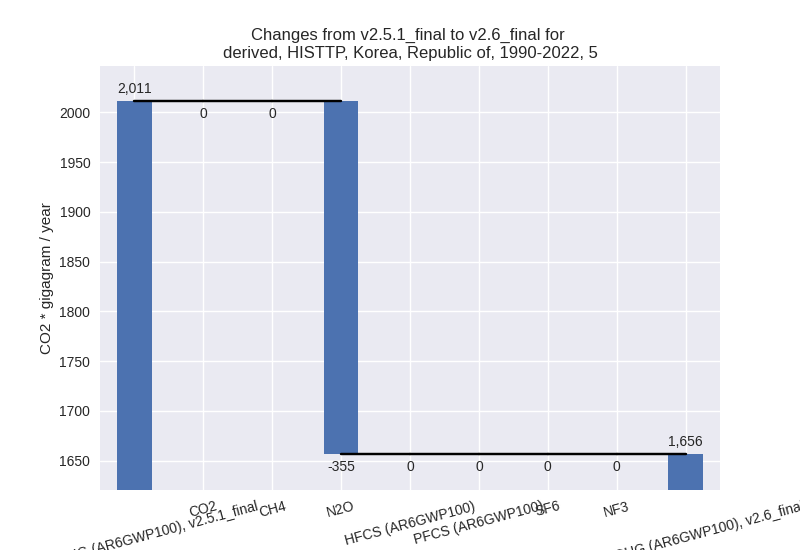
The following figures show the aggregate national total emissions excluding LULUCF AR6GWP100 for the third party priority scenario. The dotted linesshow the v2.5.1_final data.
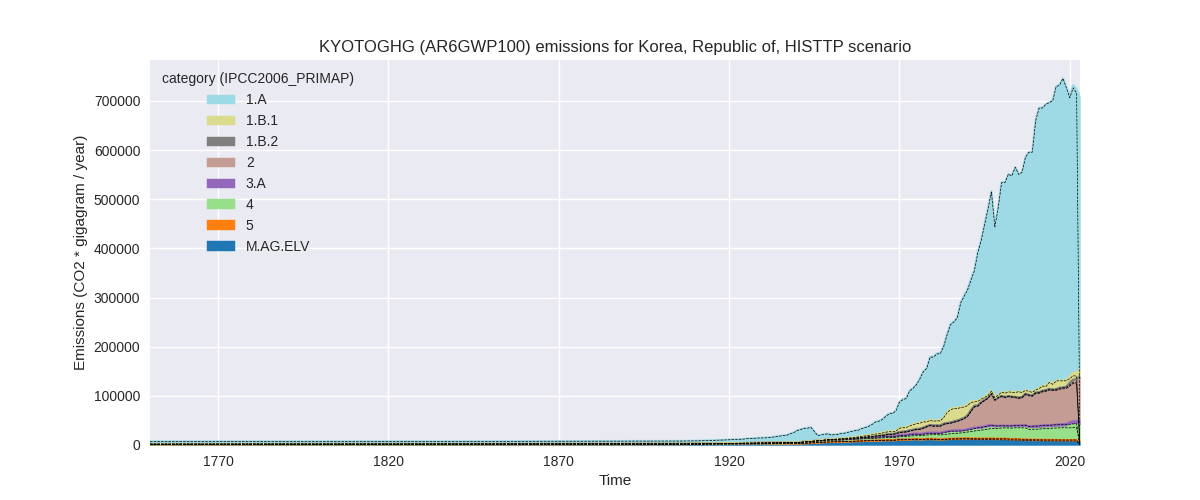
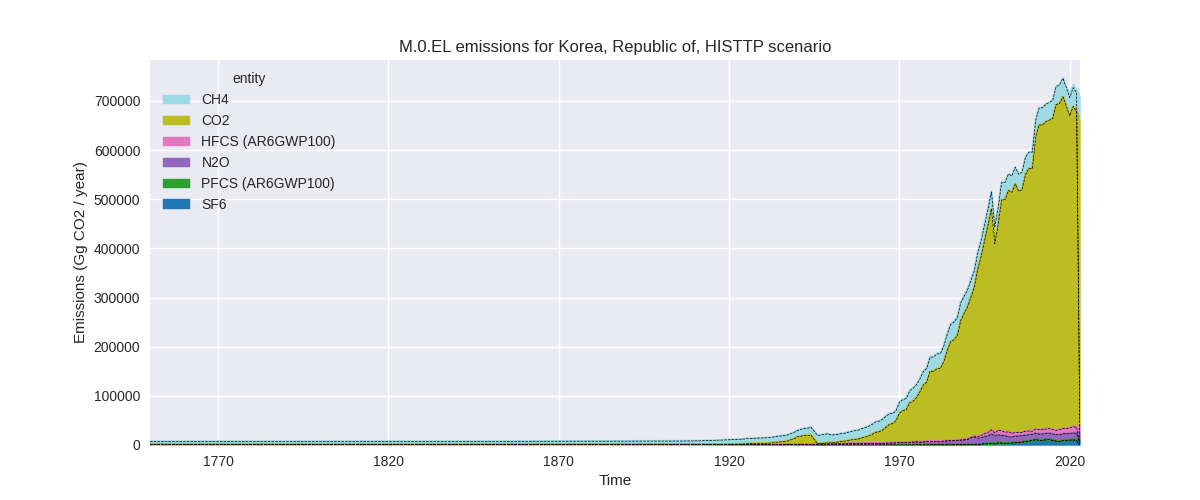
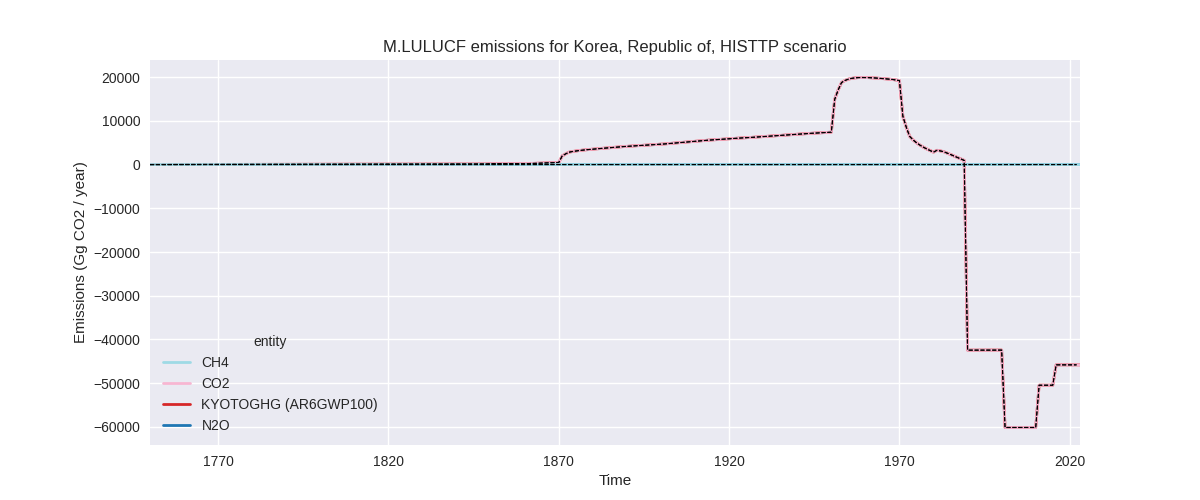
Overview over changes
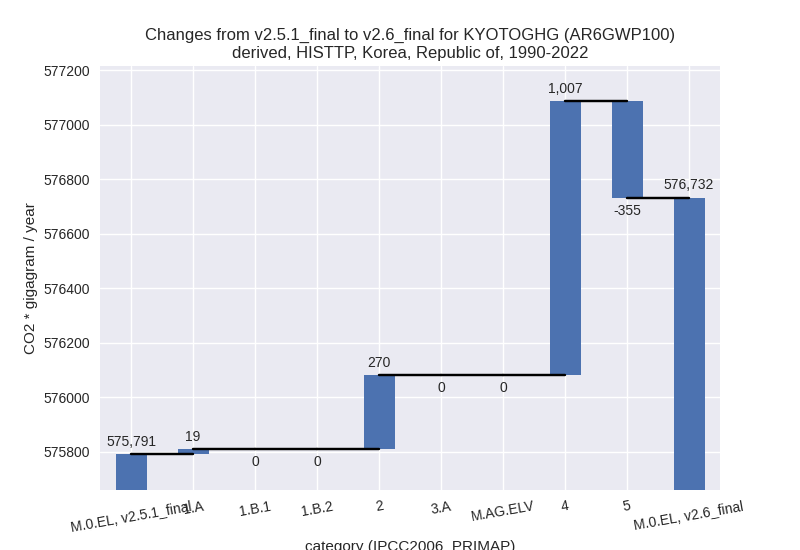
In the country reported priority scenario we have the following changes for aggregate Kyoto GHG and national total emissions excluding LULUCF (M.0.EL):
- Emissions in 2022 have changed by 0.2%% (1636.70 Gg CO2 / year)
- Emissions in 1990-2022 have changed by -0.1%% (-516.93 Gg CO2 / year)
In the third party priority scenario we have the following changes for aggregate Kyoto GHG and national total emissions excluding LULUCF (M.0.EL):
- Emissions in 2022 have changed by 1.0%% (7376.36 Gg CO2 / year)
- Emissions in 1990-2022 have changed by 0.2%% (941.04 Gg CO2 / year)
Most important changes per scenario and time frame
In the country reported priority scenario the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 2022 (top 5):
- 1: 1.A, CO2 with 3124.23 Gg CO2 / year (0.6%)
- 2: 2, HFCS (AR6GWP100) with -999.96 Gg CO2 / year (-10.2%)
- 3: 4, CH4 with -699.77 Gg CO2 / year (-5.9%)
- 4: 5, N2O with -655.65 Gg CO2 / year (-29.7%)
- 5: 1.B.2, CH4 with 408.85 Gg CO2 / year (7.4%)
In the country reported priority scenario the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 1990-2022 (top 5):
- 1: 5, N2O with -354.63 Gg CO2 / year (-17.6%)
- 2: 1.A, CO2 with -336.94 Gg CO2 / year (-0.1%)
- 3: 4, CH4 with -44.09 Gg CO2 / year (-0.4%)
- 4: 1.B.2, CH4 with 24.27 Gg CO2 / year (0.8%)
- 5: 3.A, N2O with 20.05 Gg CO2 / year (0.7%)
In the third party priority scenario the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 2022 (top 5):
- 1: 4, CH4 with 4930.61 Gg CO2 / year (21.8%)
- 2: 2, SF6 with 2014.54 Gg CO2 / year (23.0%)
- 3: 5, N2O with -655.65 Gg CO2 / year (-29.7%)
- 4: 1.A, CO2 with 455.68 Gg CO2 / year (0.1%)
- 5: 4, N2O with 200.76 Gg CO2 / year (20.1%)
In the third party priority scenario the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 1990-2022 (top 5):
- 1: 4, CH4 with 785.08 Gg CO2 / year (4.1%)
- 2: 5, N2O with -354.63 Gg CO2 / year (-17.6%)
- 3: 4, N2O with 176.55 Gg CO2 / year (20.9%)
- 4: 2, SF6 with 61.05 Gg CO2 / year (1.0%)
- 5: 4, CO2 with 44.99 Gg CO2 / year (3.5%)
Notes on data changes
Here we list notes explaining important emissions changes for the country. ’' means that the following text only applies to the TP time series, while means that it only applies to the CR scenario. Otherwise the note applies to both scenarios.
- The 2023 inventory has been included.
- Overall changes are below 1%
Changes by sector and gas
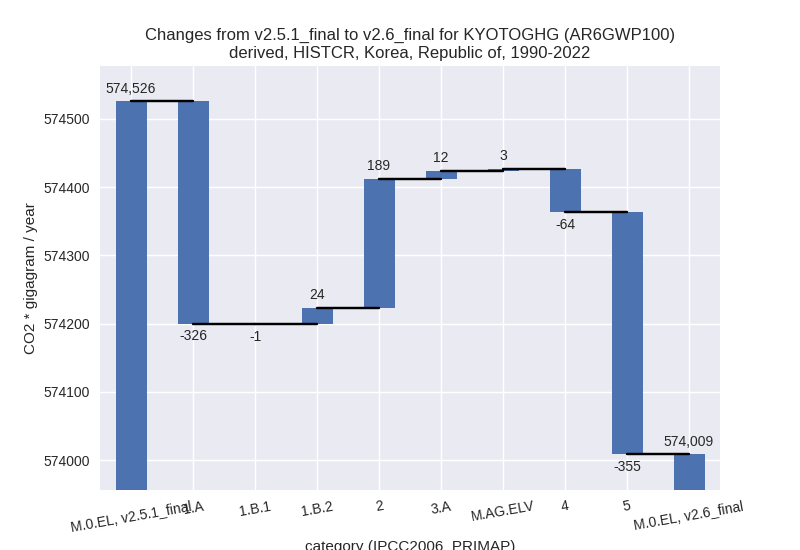
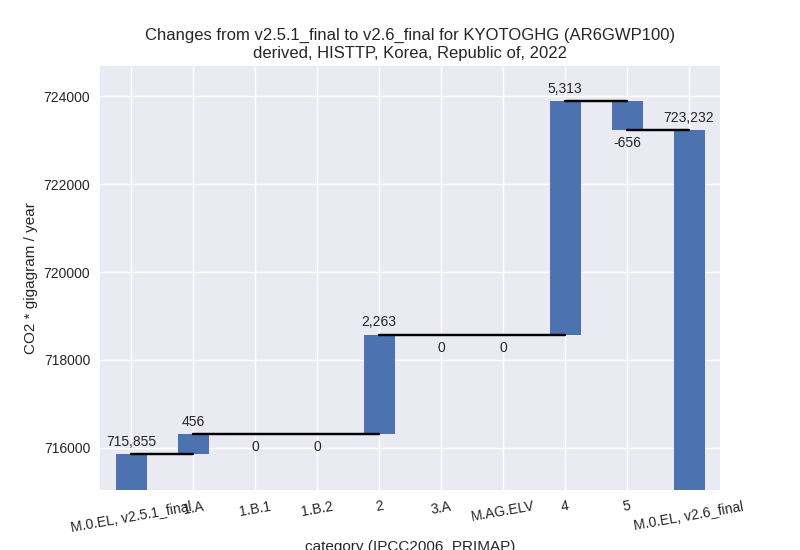
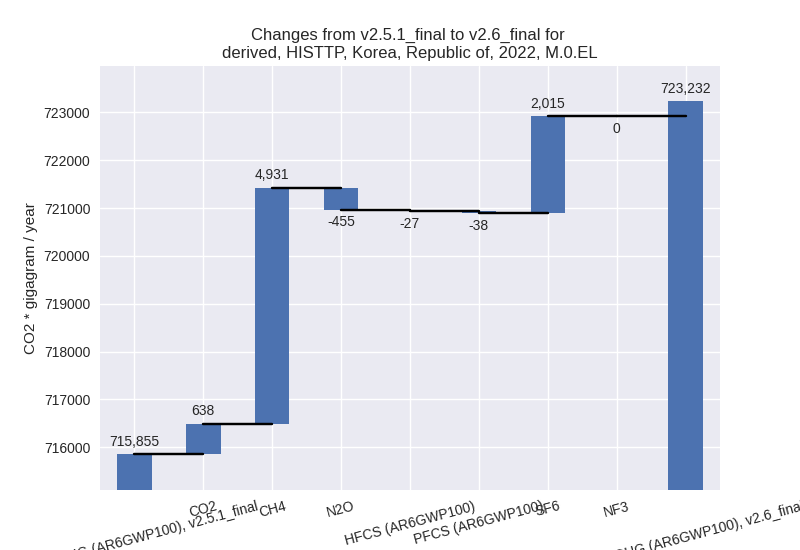
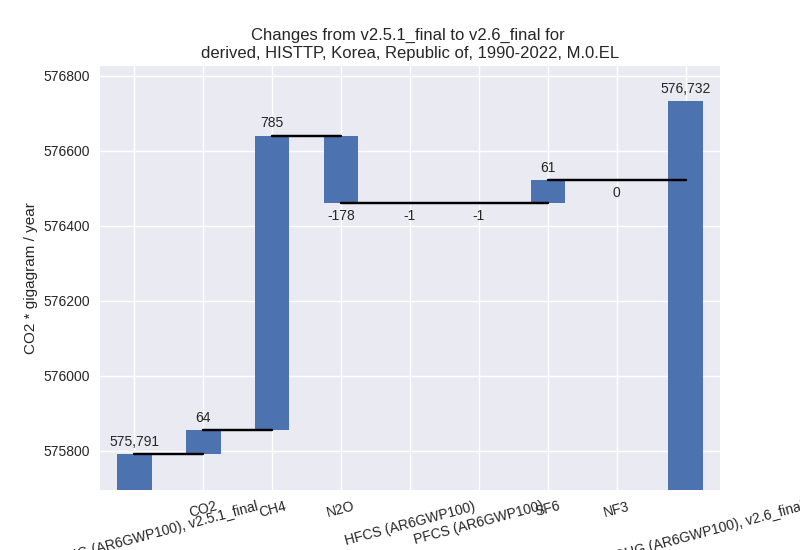
For each scenario and time frame the changes are displayed for all individual sectors and all individual gases. In the sector plot we use aggregate Kyoto GHGs in AR6GWP100. In the gas plot we usenational total emissions without LULUCF. ## country reported scenario
2022
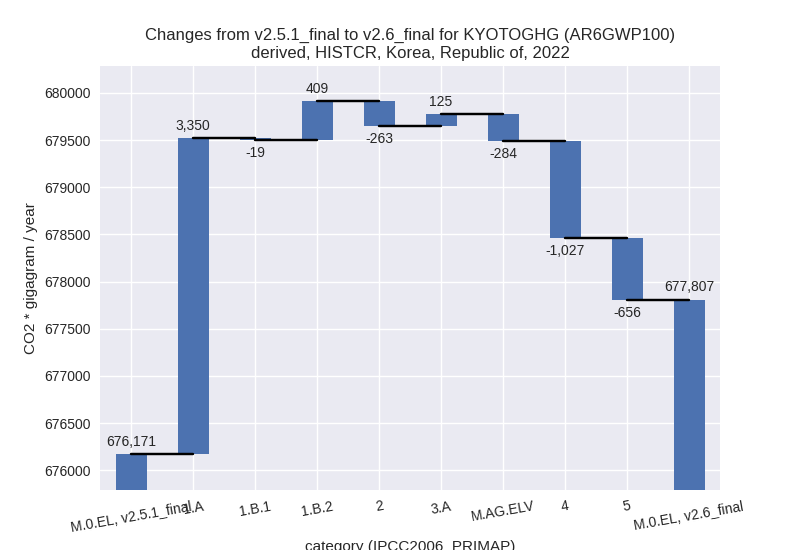
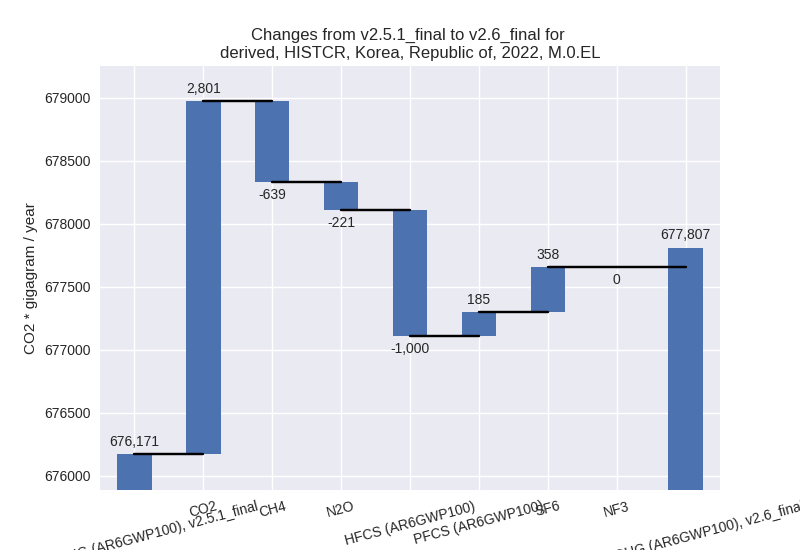
1990-2022
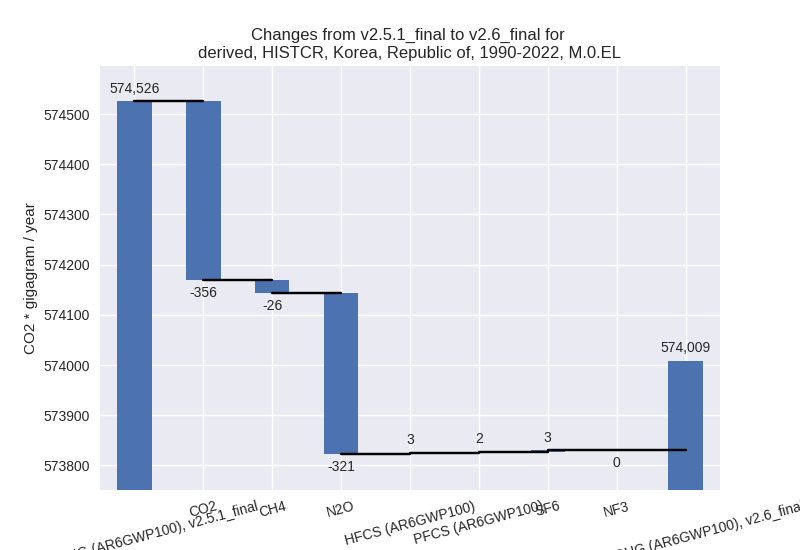
third party scenario
2022
1990-2022
Detailed changes for the scenarios:
country reported scenario (HISTCR):
Most important changes per time frame
For 2022 the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 2022 (top 5):
- 1: 1.A, CO2 with 3124.23 Gg CO2 / year (0.6%)
- 2: 2, HFCS (AR6GWP100) with -999.96 Gg CO2 / year (-10.2%)
- 3: 4, CH4 with -699.77 Gg CO2 / year (-5.9%)
- 4: 5, N2O with -655.65 Gg CO2 / year (-29.7%)
- 5: 1.B.2, CH4 with 408.85 Gg CO2 / year (7.4%)
For 1990-2022 the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 1990-2022 (top 5):
- 1: 5, N2O with -354.63 Gg CO2 / year (-17.6%)
- 2: 1.A, CO2 with -336.94 Gg CO2 / year (-0.1%)
- 3: 4, CH4 with -44.09 Gg CO2 / year (-0.4%)
- 4: 1.B.2, CH4 with 24.27 Gg CO2 / year (0.8%)
- 5: 3.A, N2O with 20.05 Gg CO2 / year (0.7%)
Changes in the main sectors for aggregate KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) are
- 1: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 579850.05 Gg CO2 / year which is 85.5% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have changed by 0.6% (3740.51 Gg CO2 / year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by -0.1% (-302.41 Gg CO2 / year).
- 2: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 53056.18 Gg CO2 / year which is 7.8% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have changed by -0.5% (-262.56 Gg CO2 / year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by 0.4% (188.91 Gg CO2 / year).
- M.AG: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 24559.86 Gg CO2 / year which is 3.6% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have changed by -0.6% (-158.99 Gg CO2 / year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by 0.1% (15.01 Gg CO2 / year).
- 4: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 18790.28 Gg
CO2 / year which is 2.8% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have
changed by -5.2% (-1026.61 Gg CO2 /
year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by -0.3% (-63.81 Gg CO2 / year). For 2022 the
changes per gas
are:
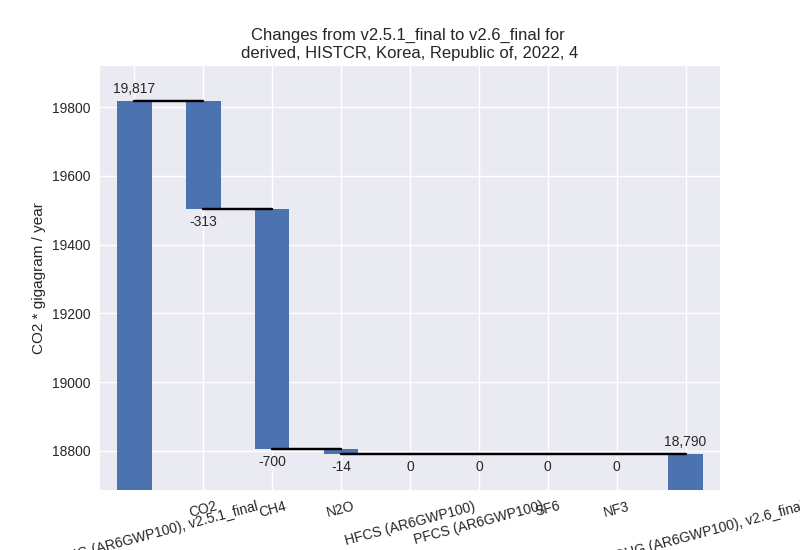
- 5: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 1550.96 Gg
CO2 / year which is 0.2% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have
changed by -29.7% (-655.65 Gg CO2 /
year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by -17.6% (-354.63 Gg CO2 / year). For 2022
the changes per gas
are:
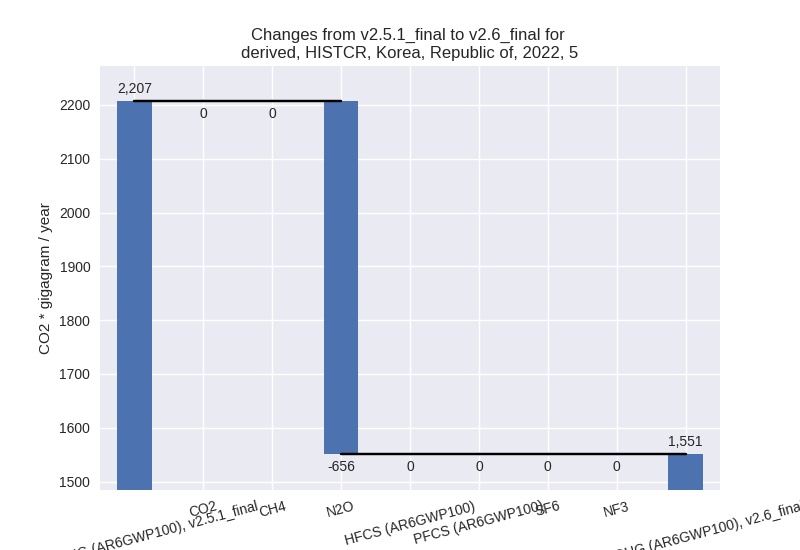
For 1990-2022 the changes per gas are: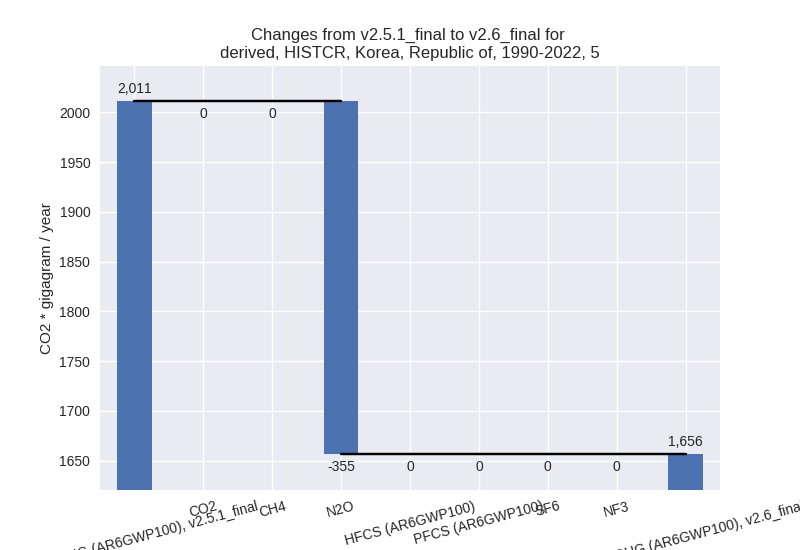
third party scenario (HISTTP):
Most important changes per time frame
For 2022 the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 2022 (top 5):
- 1: 4, CH4 with 4930.61 Gg CO2 / year (21.8%)
- 2: 2, SF6 with 2014.54 Gg CO2 / year (23.0%)
- 3: 5, N2O with -655.65 Gg CO2 / year (-29.7%)
- 4: 1.A, CO2 with 455.68 Gg CO2 / year (0.1%)
- 5: 4, N2O with 200.76 Gg CO2 / year (20.1%)
For 1990-2022 the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 1990-2022 (top 5):
- 1: 4, CH4 with 785.08 Gg CO2 / year (4.1%)
- 2: 5, N2O with -354.63 Gg CO2 / year (-17.6%)
- 3: 4, N2O with 176.55 Gg CO2 / year (20.9%)
- 4: 2, SF6 with 61.05 Gg CO2 / year (1.0%)
- 5: 4, CO2 with 44.99 Gg CO2 / year (3.5%)
Changes in the main sectors for aggregate KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) are
- 1: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 592212.13 Gg CO2 / year which is 81.9% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have changed by 0.1% (455.68 Gg CO2 / year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by 0.0% (18.96 Gg CO2 / year).
- 2: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 82933.28 Gg
CO2 / year which is 11.5% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have
changed by 2.8% (2262.88 Gg CO2 /
year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by 0.4% (270.08 Gg CO2 / year). For 2022 the
changes per gas
are:
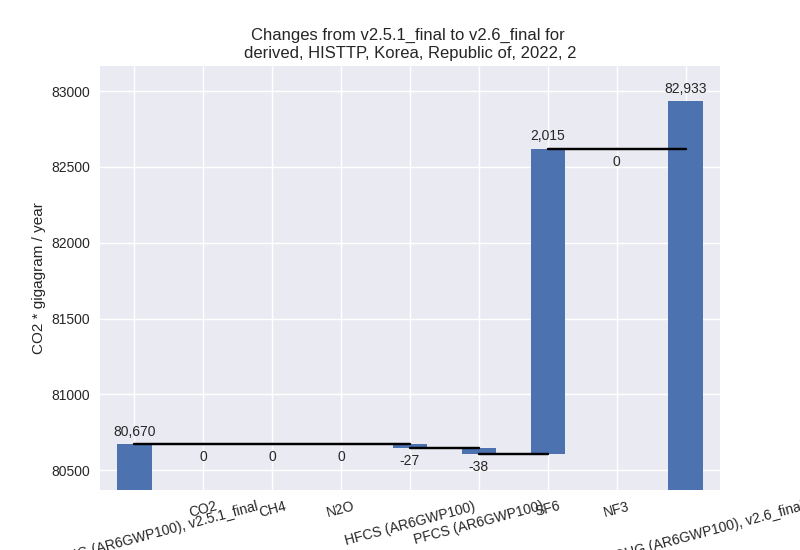
- M.AG: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 16165.44 Gg CO2 / year which is 2.2% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have changed by 0.0% (0.00 Gg CO2 / year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by 0.0% (0.00 Gg CO2 / year).
- 4: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 30369.85 Gg
CO2 / year which is 4.2% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have
changed by 21.2% (5313.46 Gg CO2 /
year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by 4.7% (1006.62 Gg CO2 / year). For 2022 the
changes per gas
are:
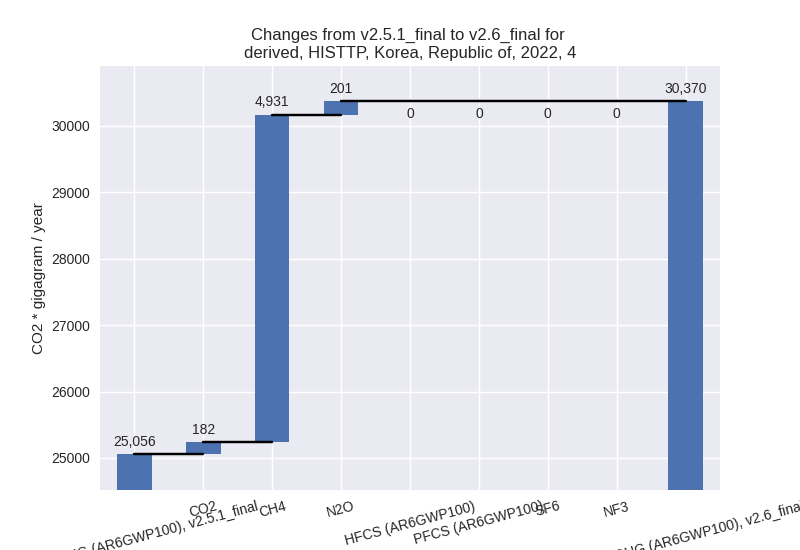
For 1990-2022 the changes per gas are: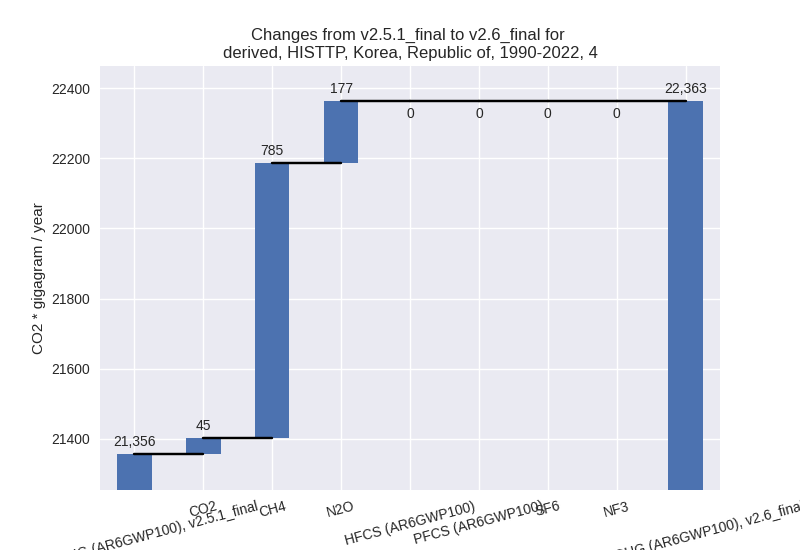
- 5: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 1550.96 Gg
CO2 / year which is 0.2% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have
changed by -29.7% (-655.65 Gg CO2 /
year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by -17.6% (-354.63 Gg CO2 / year). For 2022
the changes per gas
are:
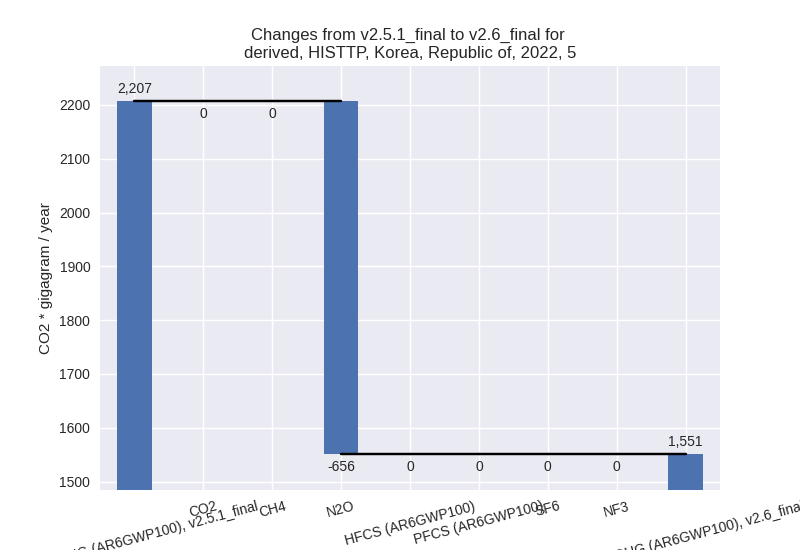
For 1990-2022 the changes per gas are: