Changes in PRIMAP-hist v2.6_final compared to v2.5.1_final for Tokelau
2024-09-24
Johannes Gütschow
Change analysis for Tokelau for PRIMAP-hist v2.6_final compared to v2.5.1_final
Overview over emissions by sector and gas
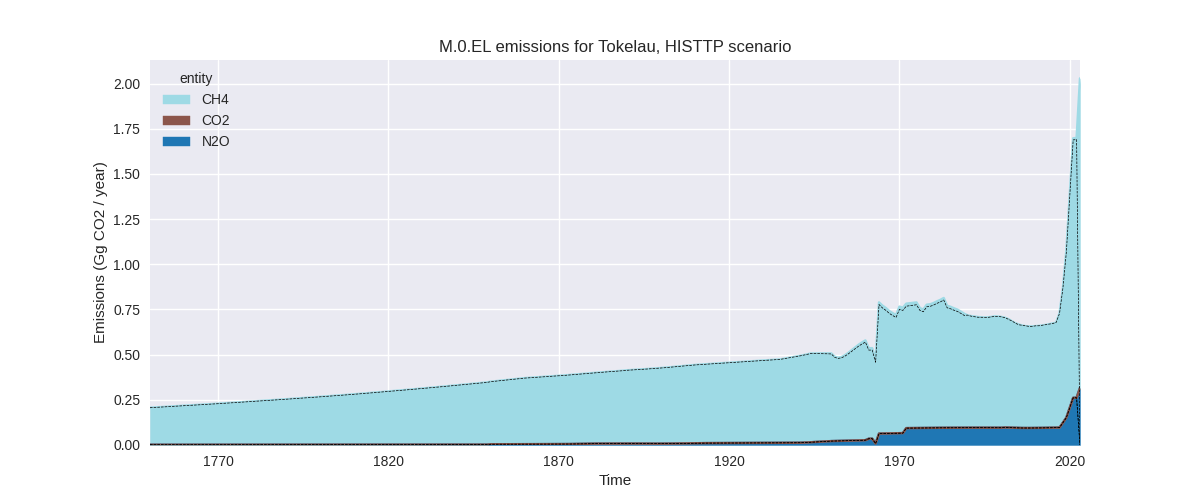
The following figures show the aggregate national total emissions excluding LULUCF AR6GWP100 for the country reported priority scenario. The dotted linesshow the v2.5.1_final data.
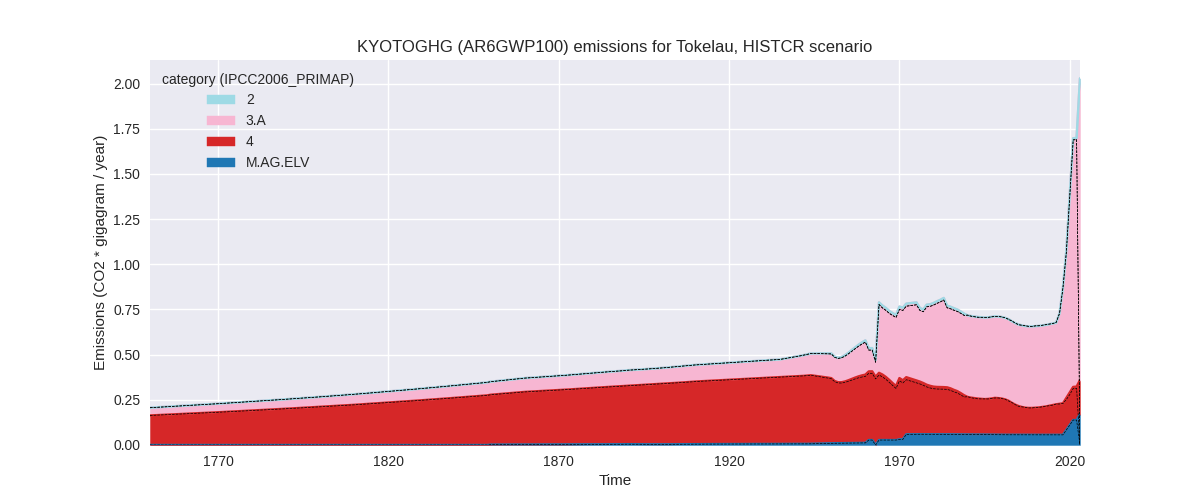
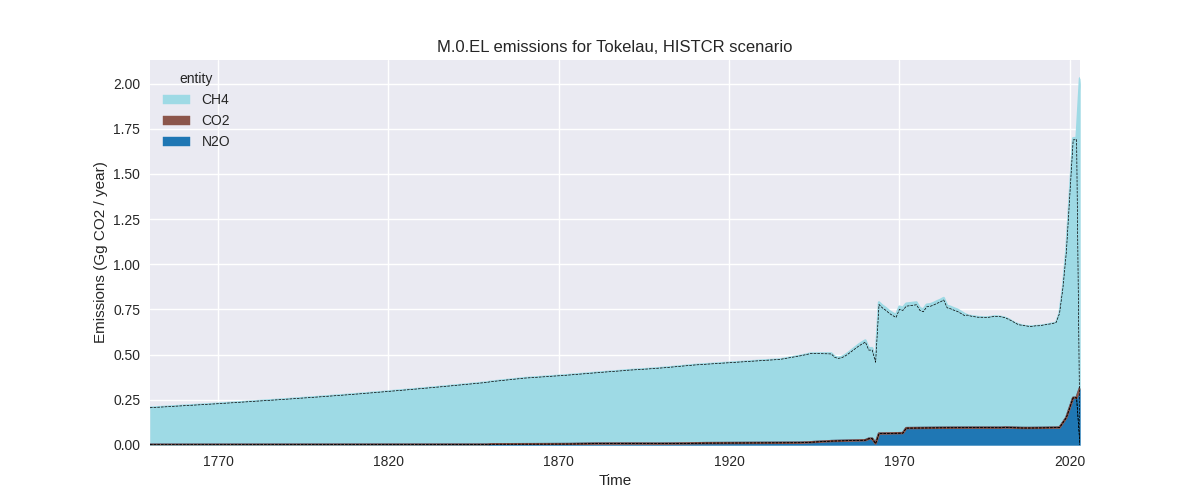
The following figures show the aggregate national total emissions excluding LULUCF AR6GWP100 for the third party priority scenario. The dotted linesshow the v2.5.1_final data.
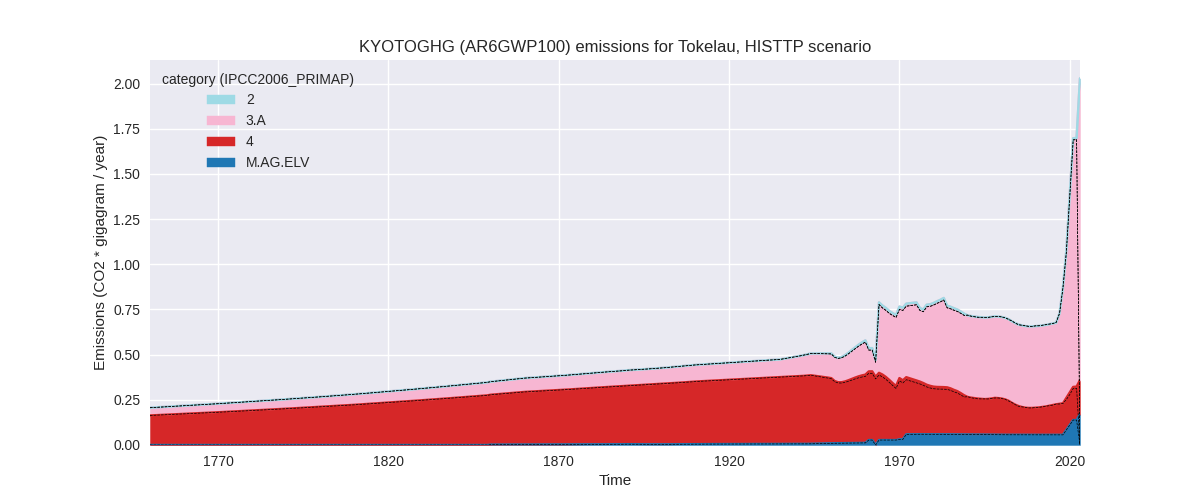
Overview over changes
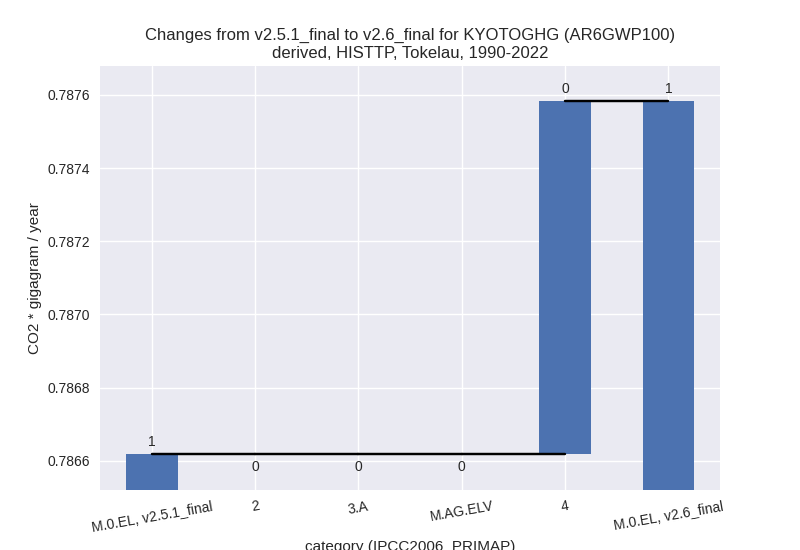
In the country reported priority scenario we have the following changes for aggregate Kyoto GHG and national total emissions excluding LULUCF (M.0.EL):
- Emissions in 2022 have changed by 0.5%% (0.01 Gg CO2 / year)
- Emissions in 1990-2022 have changed by 0.1%% (0.00 Gg CO2 / year)
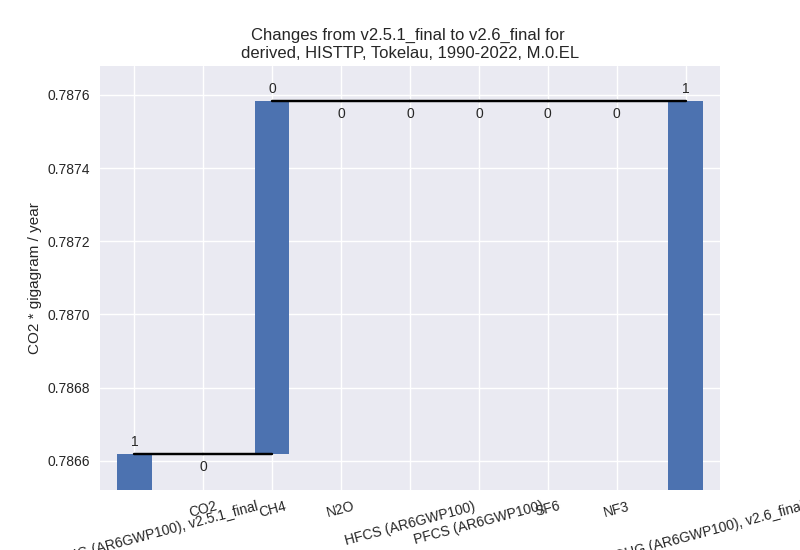
In the third party priority scenario we have the following changes for aggregate Kyoto GHG and national total emissions excluding LULUCF (M.0.EL):
- Emissions in 2022 have changed by 0.5%% (0.01 Gg CO2 / year)
- Emissions in 1990-2022 have changed by 0.1%% (0.00 Gg CO2 / year)
Most important changes per scenario and time frame
In the country reported priority scenario the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 2022 (top 5):
- 1: 4, CH4 with 0.01 Gg CO2 / year (5.6%)
- 2: 3.A, CH4 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 3: M.AG.ELV, CH4 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 4: 2, CO2 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 5: 3.A, N2O with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
In the country reported priority scenario the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 1990-2022 (top 5):
- 1: 4, CH4 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.6%)
- 2: 3.A, CH4 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 3: M.AG.ELV, CH4 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 4: 2, CO2 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 5: 3.A, N2O with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
In the third party priority scenario the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 2022 (top 5):
- 1: 4, CH4 with 0.01 Gg CO2 / year (5.6%)
- 2: 3.A, CH4 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 3: M.AG.ELV, CH4 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 4: 2, CO2 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 5: 3.A, N2O with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
In the third party priority scenario the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 1990-2022 (top 5):
- 1: 4, CH4 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.6%)
- 2: 3.A, CH4 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 3: M.AG.ELV, CH4 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 4: 2, CO2 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 5: 3.A, N2O with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
Notes on data changes
No country specific notes present for this changelog.
Changes by sector and gas
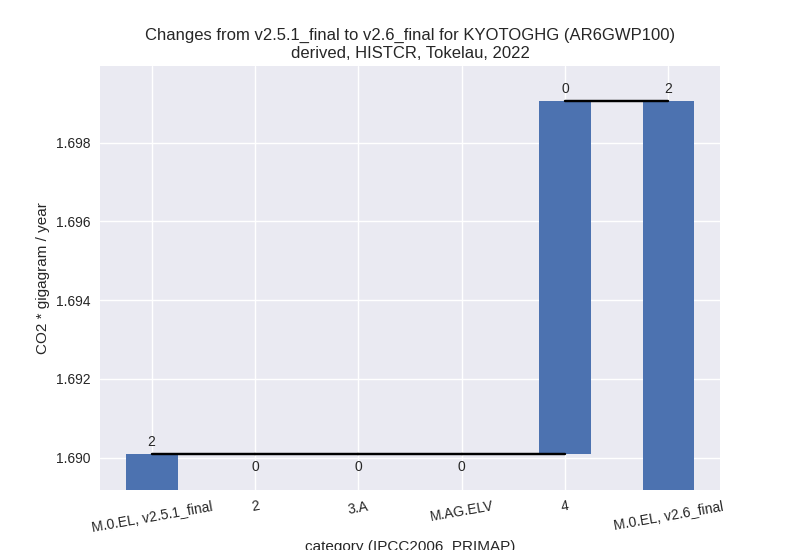
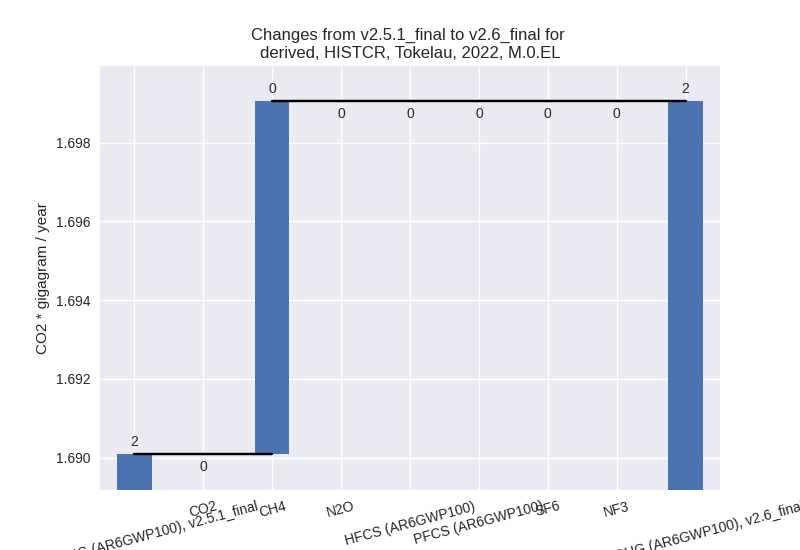
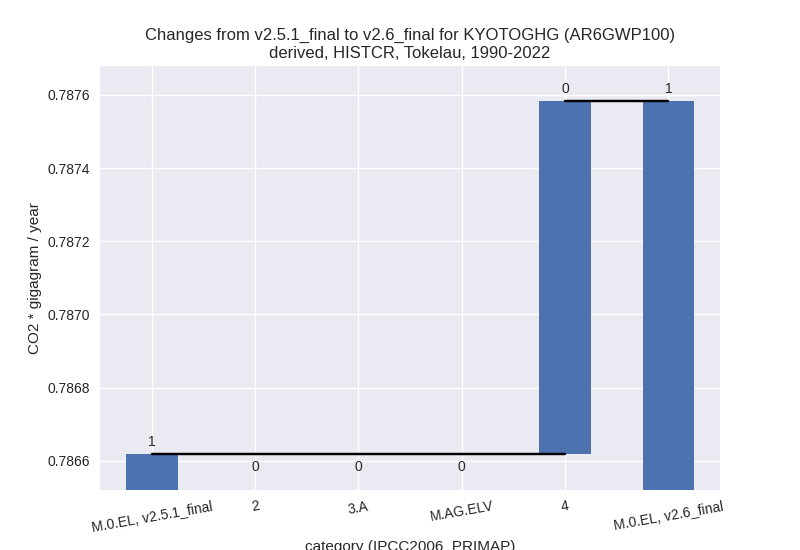
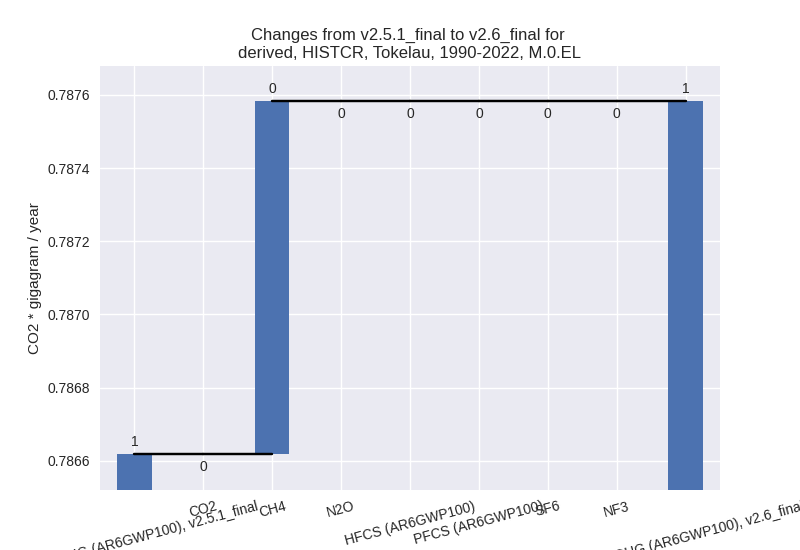
For each scenario and time frame the changes are displayed for all individual sectors and all individual gases. In the sector plot we use aggregate Kyoto GHGs in AR6GWP100. In the gas plot we usenational total emissions without LULUCF. ## country reported scenario
2022
1990-2022
third party scenario
2022
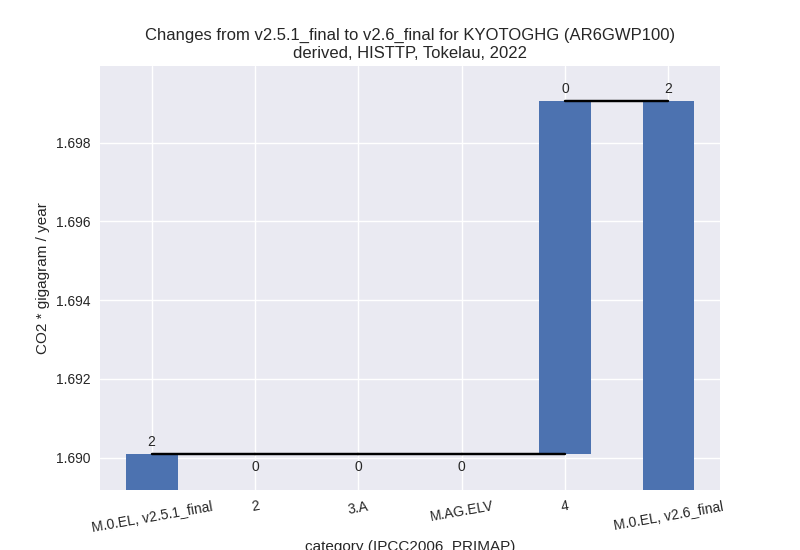
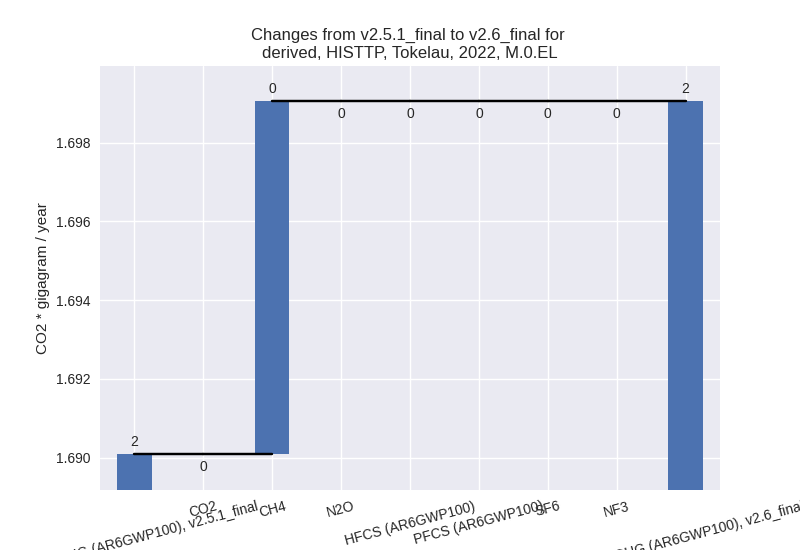
1990-2022
Detailed changes for the scenarios:
country reported scenario (HISTCR):
Most important changes per time frame
For 2022 the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 2022 (top 5):
- 1: 4, CH4 with 0.01 Gg CO2 / year (5.6%)
- 2: 3.A, CH4 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 3: M.AG.ELV, CH4 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 4: 2, CO2 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 5: 3.A, N2O with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
For 1990-2022 the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 1990-2022 (top 5):
- 1: 4, CH4 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.6%)
- 2: 3.A, CH4 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 3: M.AG.ELV, CH4 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 4: 2, CO2 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 5: 3.A, N2O with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
Changes in the main sectors for aggregate KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) are
1: No data
2: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 0.00 Gg CO2 / year which is 0.0% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have changed by 0.0% (0.00 Gg CO2 / year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by 0.0% (0.00 Gg CO2 / year).
M.AG: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 1.51 Gg CO2 / year which is 89.1% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have changed by 0.0% (0.00 Gg CO2 / year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by 0.0% (0.00 Gg CO2 / year).
4: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 0.19 Gg CO2 / year which is 10.9% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have changed by 5.1% (0.01 Gg CO2 / year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by 0.5% (0.00 Gg CO2 / year). For 2022 the changes per gas are:
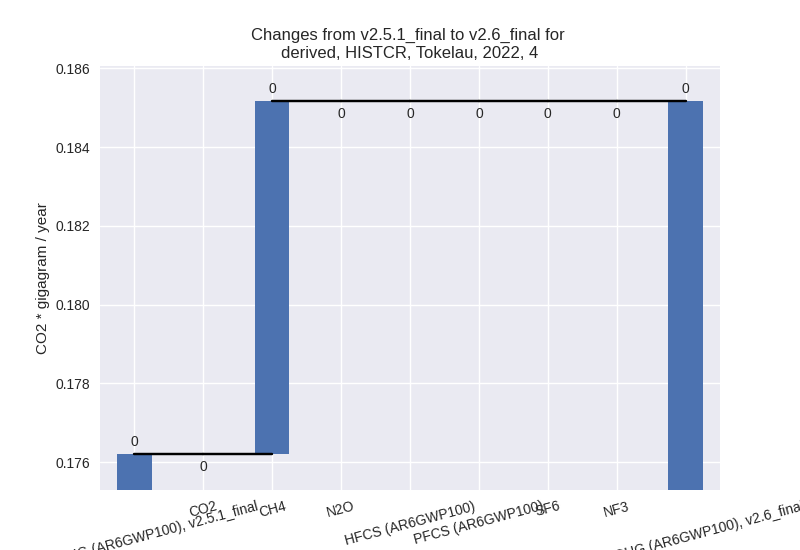
5: No data
third party scenario (HISTTP):
Most important changes per time frame
For 2022 the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 2022 (top 5):
- 1: 4, CH4 with 0.01 Gg CO2 / year (5.6%)
- 2: 3.A, CH4 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 3: M.AG.ELV, CH4 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 4: 2, CO2 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 5: 3.A, N2O with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
For 1990-2022 the following sector-gas combinations have the highest absolute impact on national total KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) emissions in 1990-2022 (top 5):
- 1: 4, CH4 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.6%)
- 2: 3.A, CH4 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 3: M.AG.ELV, CH4 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 4: 2, CO2 with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
- 5: 3.A, N2O with 0.00 Gg CO2 / year (0.0%)
Changes in the main sectors for aggregate KyotoGHG (AR6GWP100) are
1: No data
2: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 0.00 Gg CO2 / year which is 0.0% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have changed by 0.0% (0.00 Gg CO2 / year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by 0.0% (0.00 Gg CO2 / year).
M.AG: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 1.51 Gg CO2 / year which is 89.1% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have changed by 0.0% (0.00 Gg CO2 / year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by 0.0% (0.00 Gg CO2 / year).
4: Total sectoral emissions in 2022 are 0.19 Gg CO2 / year which is 10.9% of M.0.EL emissions. 2022 Emissions have changed by 5.1% (0.01 Gg CO2 / year). 1990-2022 Emissions have changed by 0.5% (0.00 Gg CO2 / year). For 2022 the changes per gas are:
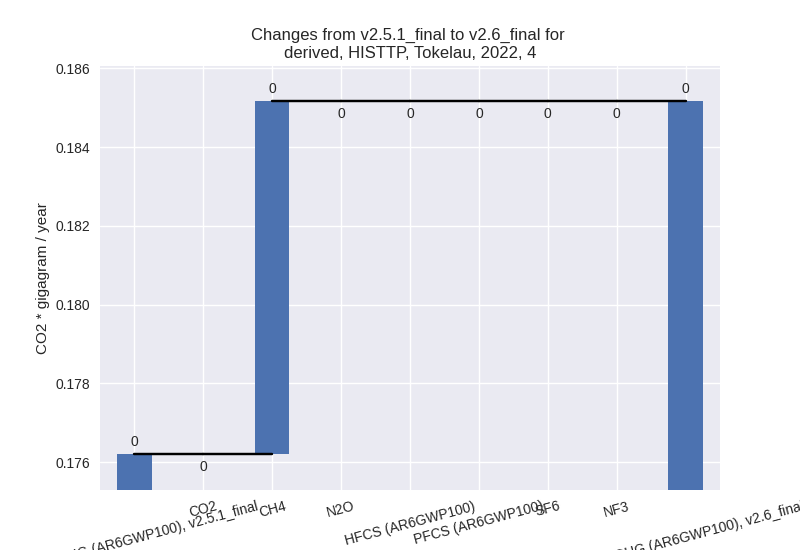
5: No data